Greenhouse Gas Definition Biology
It also occurs naturally as it flows in a cycle between oceans, soil, plants and animals.

Greenhouse gas definition biology. Greenhouse effect Planetary warming as a result of the trapping of solar energy beneath atmospheric gases. A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. (1986).4 A more detailed discussion of biology and variables affecting.
Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer. In a molecule of carbon dioxide, there is one atom of carbon bonded with two atoms of oxygen.
Absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the. At its simplest, biotechnology is technology based on biology - biotechnology harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products that help improve our lives and the health of our planet. This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases.
The sun's energy enters but infrared energy is trapped. Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such. They are absorb most of the heat that would normally be radiat….
These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. Definition of greenhouse gas :. Fossil fuel combustion, which has increased at a rapid rate since the 1950s, has.
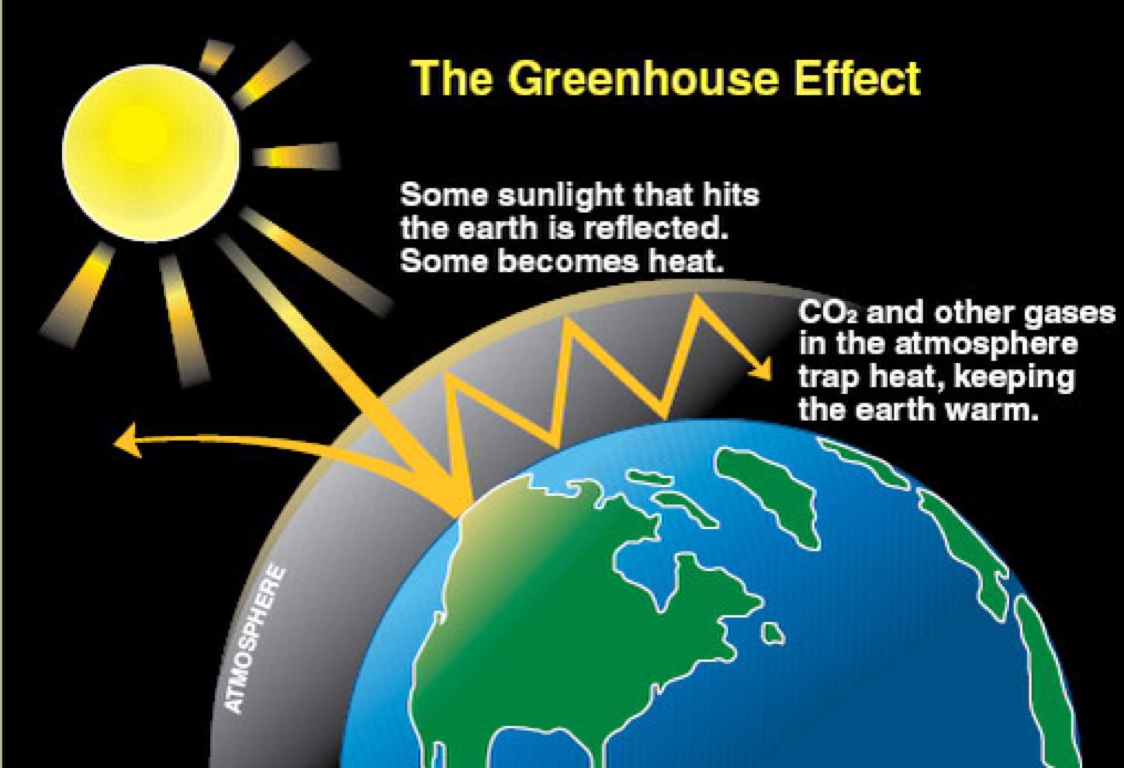
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere. A lot of the sun’s energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space. At night there would nothing to keep the energy in and we'd be….
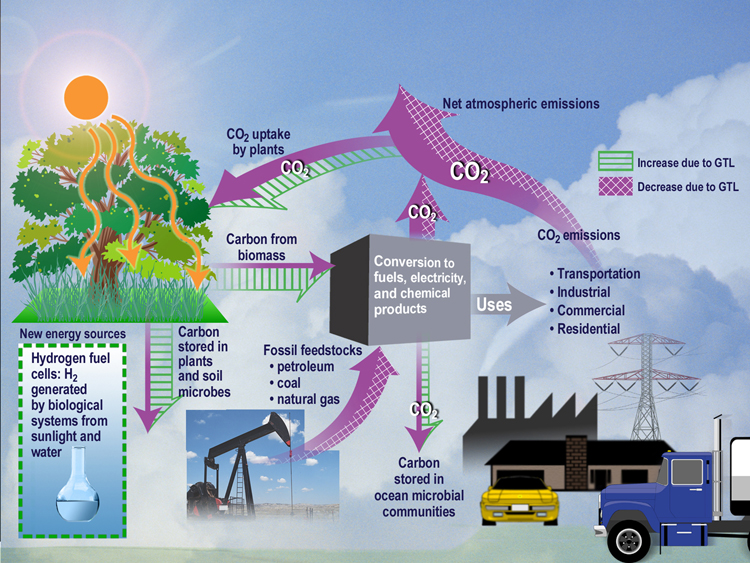
The carbon cycle is composed of natural sinks and sources of carbon, which can be manipulated to favor removal of CO 2 from the atmosphere, or may be perturbed by human greenhouse gas emissions or attempts to sequester carbon to reduce atmospheric CO 2. Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. Students explore the greenhouse effect through computer simulations and then dive deeper learning how the greenhouse effect works via readings and videos online.
The Journal publishes results of experimental and pilot studies, technology demonstrations, process design and. So regardless of one's precise definition of DAI, stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations much above 450 ppm CO 2 eq would be a terribly risky prospect. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat just like the glass roof of a greenhouse.
EPA Office of Policy, Planning and Evaluation (OPPE),2 International Anthropogenic Methane Emissions:. Formed from the decomposition of long-ago living organisms. Balanced between the energy it gets from the sun and the energ….
The two major greenhouse gases both occur naturally and can be increased due to human activity. They're called Greenhouse gasesand they include water vapou…. The composition and concentration of the gases in the atmosphere influence the earth's surface temperature because some gases more effectively retain heat than others.
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides. Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets.
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today far exceeds the natural range seen over the last 650,000 years. A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared radiation (IR) and radiates heat in all directions. Accomplishing 450 ppm CO 2 eq stabilization will require bringing global emissions to a peak within the next decade, and to ≈50% of the their 00 levels by mid-century ( 12 ).
Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century. Supplement Examples of greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, ozone and fluorocarbons. Greenhouse effect definition is - warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface.
Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and energy Supplement Methanotrophs are organisms that require methane as a source of carbon and energy for their metabolism.They are gram-negative bacteria that are capable in utilizing methane as a carbon energy source and able to grow both aerobically or anaerobically which only need single. Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect.
The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3). Responsible for 63 percent of global warming over time, and 91 percent in the last 5 years, this gas is produced from burning fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. We have used the biological processes of microorganisms for more than 6,000 years to make useful….
Gases that absorb heat in the atmosphere near the Earth's surface, preventing it from escaping into space. The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them. A gas that causes the….
Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time. Some gases, when present in the atmosphere, absorb that reflected energy and redirect it back to Earth as heat. This trapped heat creates the greenhouse effect, which in turn, contributes to climate change.
An atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by short-wave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longer-wavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;. Global Warming Definition “Global warming is a gradual increase in the earth’s temperature generally due to the greenhouse effect caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants. Professor M Mercedes Maroto-Valer and Dr Curtis M.
But, greenhouse gases may have been added to an atmosphere by an asteroid impact, volcanic activity, or even massive forest fires. We need a global system for limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight.
Radiatively active gases (i.e., greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions. What Is The Greenhouse Effect And How Does It Cause Climate Change The greenhouse effect is caused by our atmosphere The greenhouse gases that are present in our atmosphere, such as water vapor, CO 2 , ozone and methane create a “shield” that traps the heat around our planet. Waste product of combustion & decompostion.
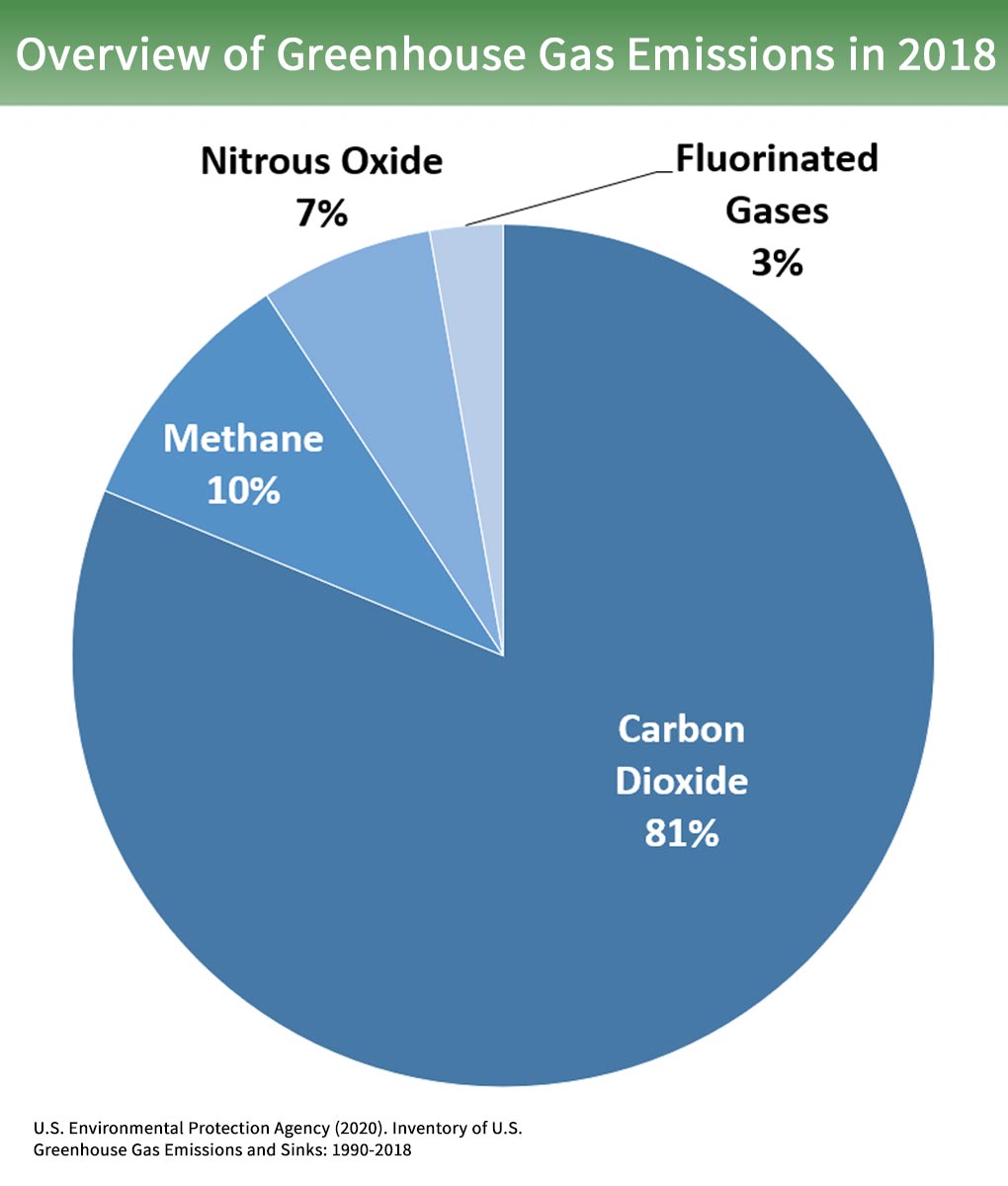
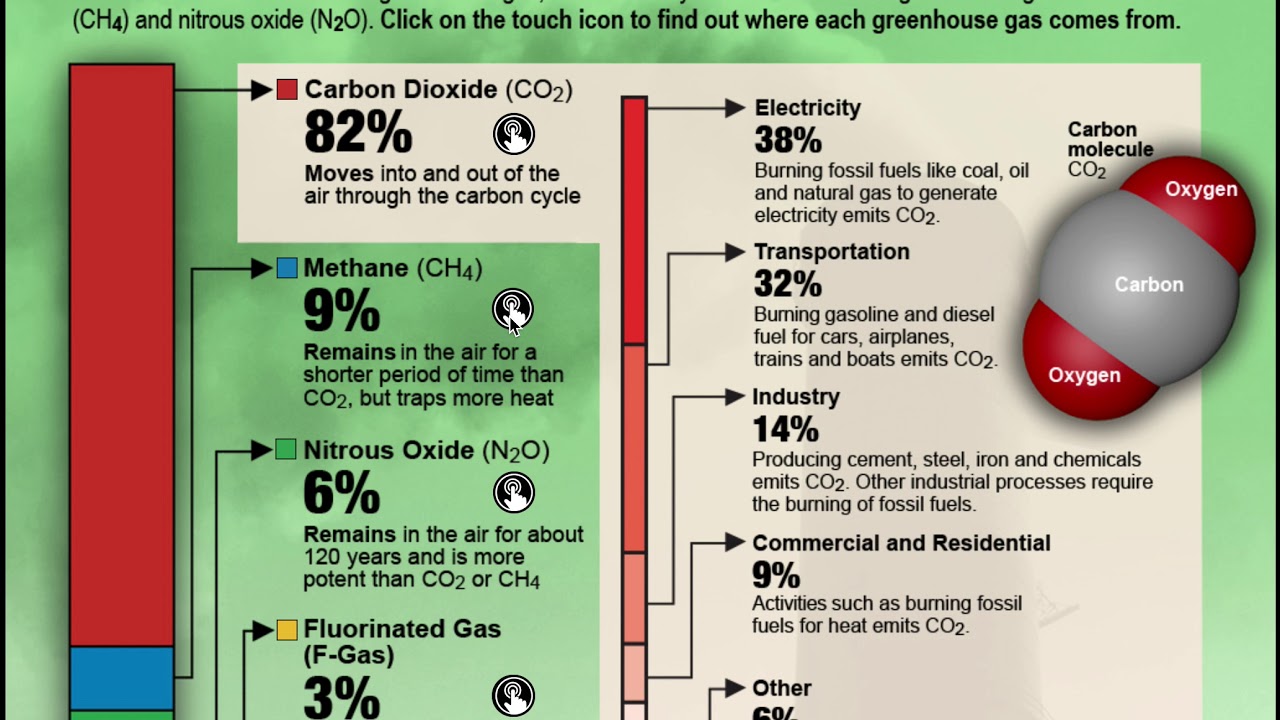
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases. 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time. Greenhouse gases are not.
Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space. The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun.
Thinking is a process that takes place (or which can take place) in. Greenhouse Gases at EPA Before there were federal requirements to do so, EPA had developed a greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions inventory and established reduction targets to decrease its GHG footprint. So in essence, a greenhouse gas is simply any atmospheric gas that traps heat within the atmosphere.
Methodologies for Estimating Greenhouse Gas Emissions, prepared by the U. A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere. One of several gases, especially carbon dioxide, that prevent heat from the earth escaping into space, causing the greenhouse effect:.
The main greenhouse gases. Whatever the cause, during this warming episode temperatures rose drastically. Greenhouse gases allow the sun’s light to shine onto Earth’s surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth’s atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it. Students will learn how greenhouse gases temporarily trap heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming our planet via the greenhouse effect.
The Greenhouse Without Tomatoes:. Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperature, precipitation, wind patterns and other measures of climate that occur over several decades or longer. 78/112 (Energy & Fuels) 40/53 (Engineering, Environmental) 161/265 (Environmental Sciences).
In its atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder on average than it is now. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. 19 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics):.
Estimates for 1990,3 and Crutzen, et al. Carbon dioxide (CO2) fossil fuels. A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere.
Learn about BIO, register for events and explore member services. The International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control is a peer reviewed journal focusing on applied science and engineering advances in control of greenhouse gas emissions and reductions of their atmospheric concentrations through carbon dioxide capture, transport and storage. This is a good example of what can happen.
If the atmospheric concentrations of these gases rise, the average temperature of the lower atmosphere will gradually increase, a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect. Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surface. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air.
Radical steps to reduce greenhouse gases will have a huge effect on the economy. The Biotechnology Innovation Organization is the world's largest biotech trade association. A complex system (CS) is defined as a set of elements, with connections between them, singled out of the environment, capable of getting information from the environment, capable of making decisions (i.e., of choosing between alternatives), and having purposefulness (i.e., an urge towards preferable states or other goals).
There are three types of GHG emissions EPA tracks and works to reduce. Definition noun Any of the atmospheric gases responsible for the greenhouse effect. The ability of certain gases, greenhouse gases, to be transparent to inbound visible light from the sun, yet opaque to the energy radiated from the earth is one of the best still events in the.
Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth. During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. The chemical formula for carbon dioxide is CO2, and a molecular model looks like this:.
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere. Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed with concern.
Carbon dioxide (CO 2):. A gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2. They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
What are the gases that keep the energy…. Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane.
Much of the Earth became desert, and over 90% of all species living at that time went extinct. Feed production includes all the greenhouse gas emission arising from 1) land use change, 2) manufacturing and use of fertilizers and pesticides, 3) manure excreted and applied to fields, 4) agricultural operations, 5) feed processing, and 6) feed transport.Although these processes result in a large share of the livestock supply chain, in this article, we mainly focus on direct livestock. The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement adopted in 1997 that aimed to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and the presence of greenhouse gases.

Greenhouse Gases Emissions From Wastewater Treatment Plants Minimization Treatment And Prevention
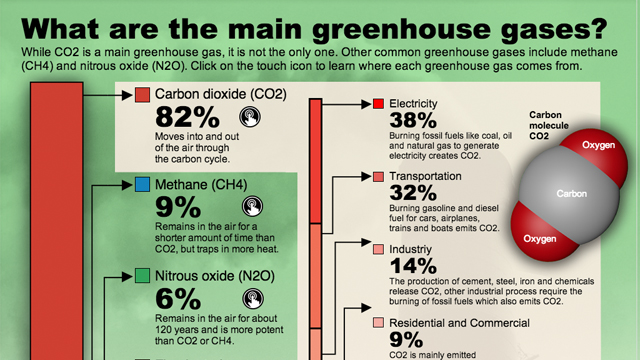
What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed

Planktonic Algae Definition Glossary Details Oilgae Greenhouse Gases Biology Class Glossary
Greenhouse Gas Definition Biology のギャラリー

Earth System Modeling A Definition Climateurope

The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society
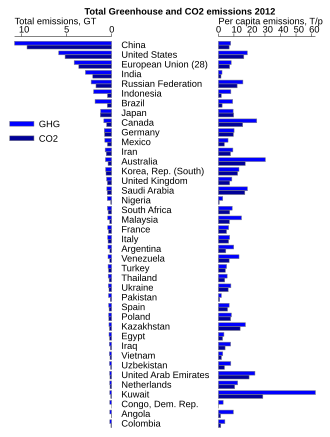
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming
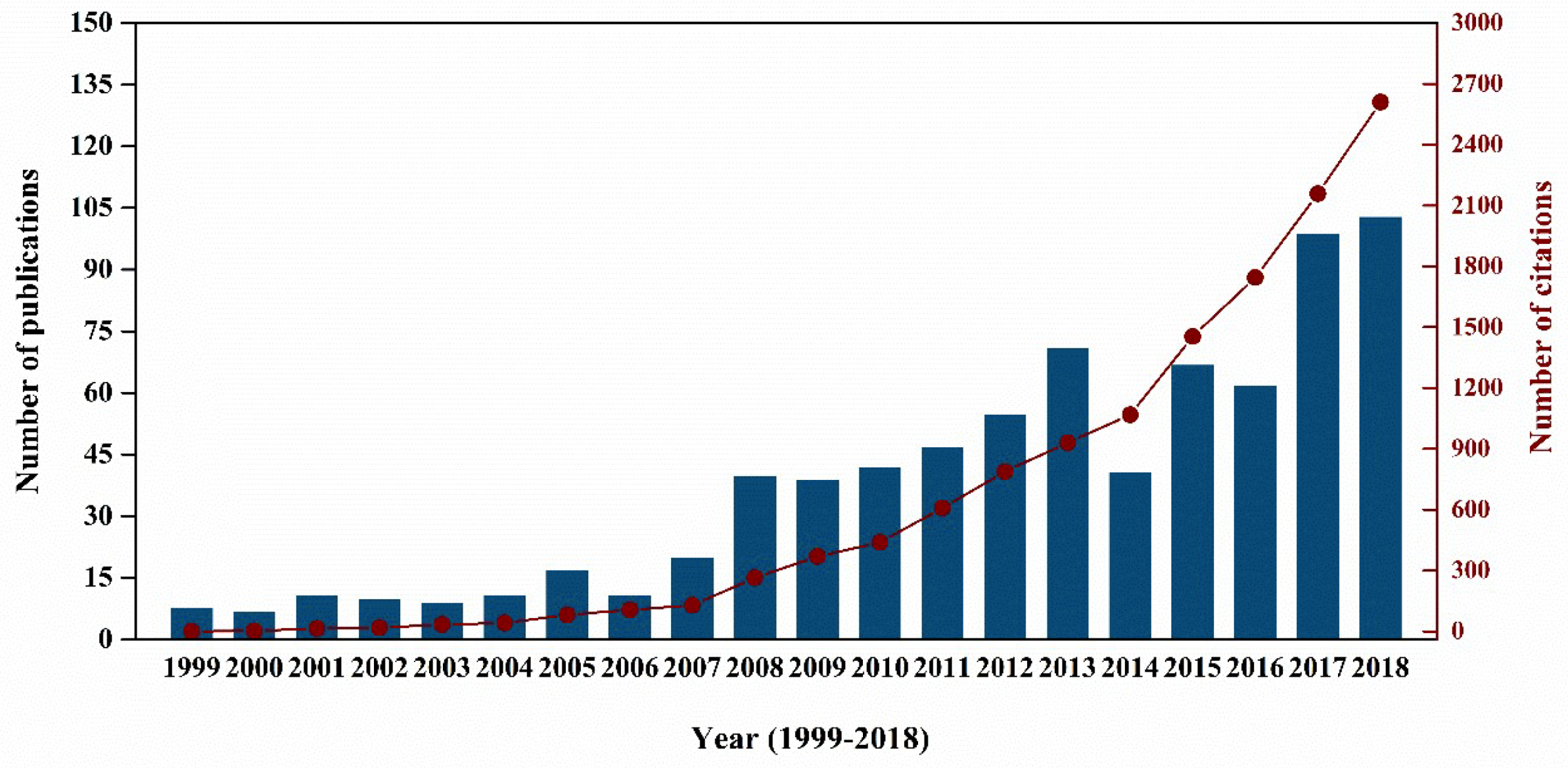
Sustainability Free Full Text Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Landfills A Review And Bibliometric Analysis
Youth Ag Greenhouse Gas Educational Lab Materials Via Pork Producti
What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic

Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society

Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation
What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed

Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Presented By Mamoona Ghaffar Docsity

Bio 304 Study Areas Examl Chapters 1 8 Essentials Chegg Com

Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
/smoke-and-coal-plant-smokestacks-520518812-584ac8125f9b58a8cd0e87c8.jpg)
Carbon Dioxide The No 1 Greenhouse Gas
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrkshs4yxsmfkaj 7o4ctqd2sjucsgee2fpvlscwmrhqroqc Usqp Cau

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions

What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Does Sustainability Mean Greenhouse Gases Mr Palmer S Geography History

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
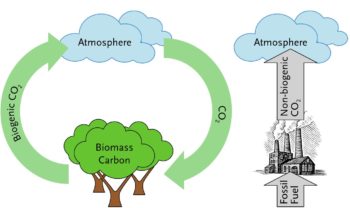
Fossil Vs Biogenic Co2 Emissions Bioenergy

Air Pollution

Definition Of Regenerative Agriculture How It Benefits Climate Change

Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences

Global Warming Key Words Combustion Carbon Dioxide Methane Deforestation Ppt Video Online Download

Greenhouse Gases Bioninja

Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Soils A Review Sciencedirect

Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsacfivl5yiym1z15qpgc24i5ya0kio Ipgu6d Zzdrtujy0gne Usqp Cau
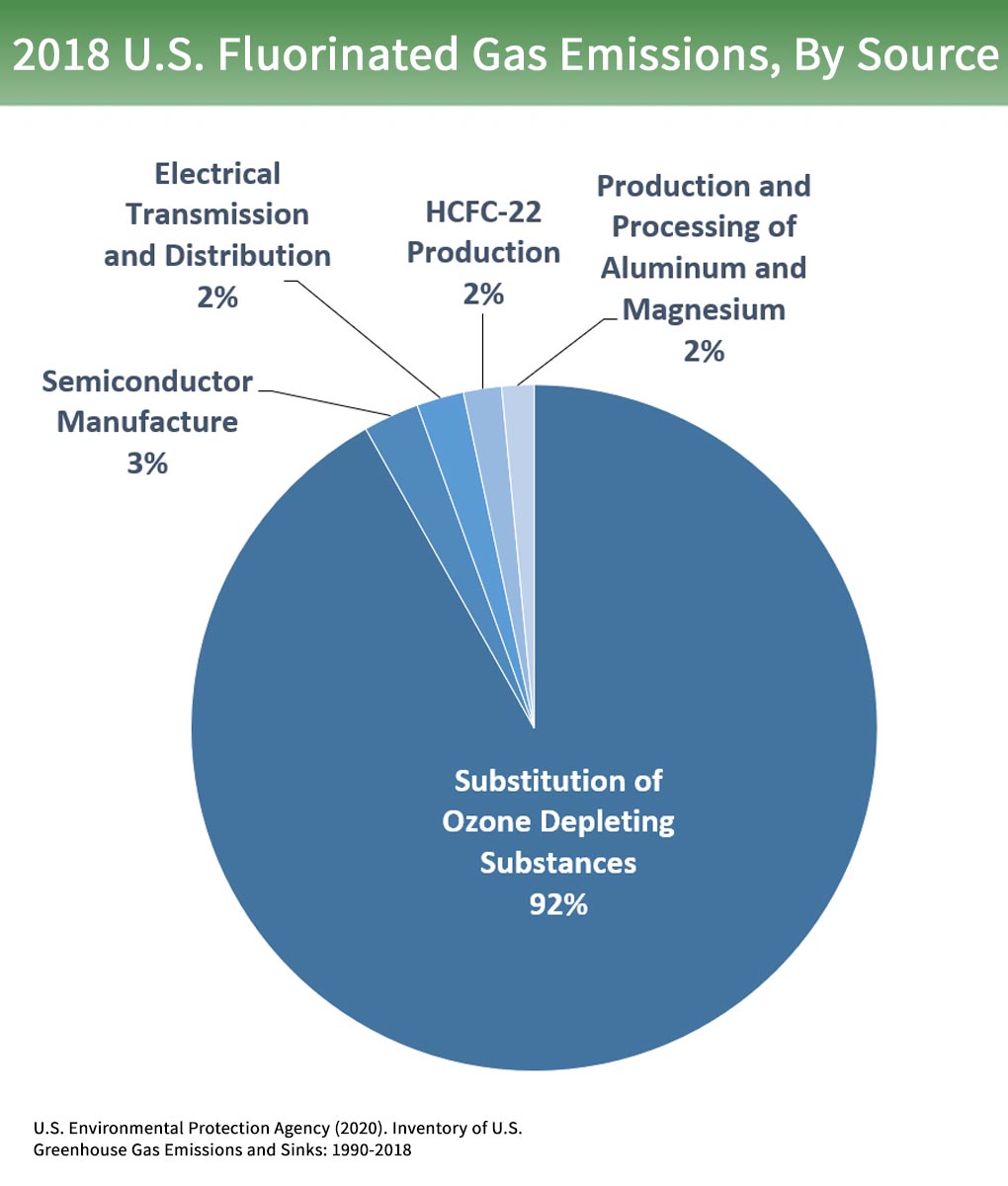
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
2

Livestock Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Mitigation Potential In Europe Bellarby 13 Global Change Biology Wiley Online Library

The Greenhouse Effect Videos Causes Mechanism With Case Studies

Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

934 Questions With Answers In Carbon Dioxide Science Topic

The Ocean A Carbon Sink Ocean Climate Platform

Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Presented By Mamoona Ghaffar Docsity
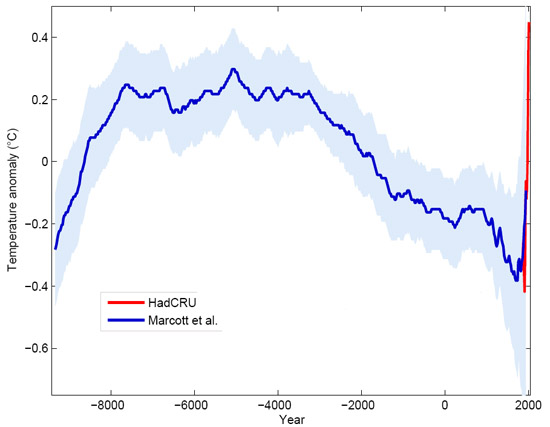
The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect
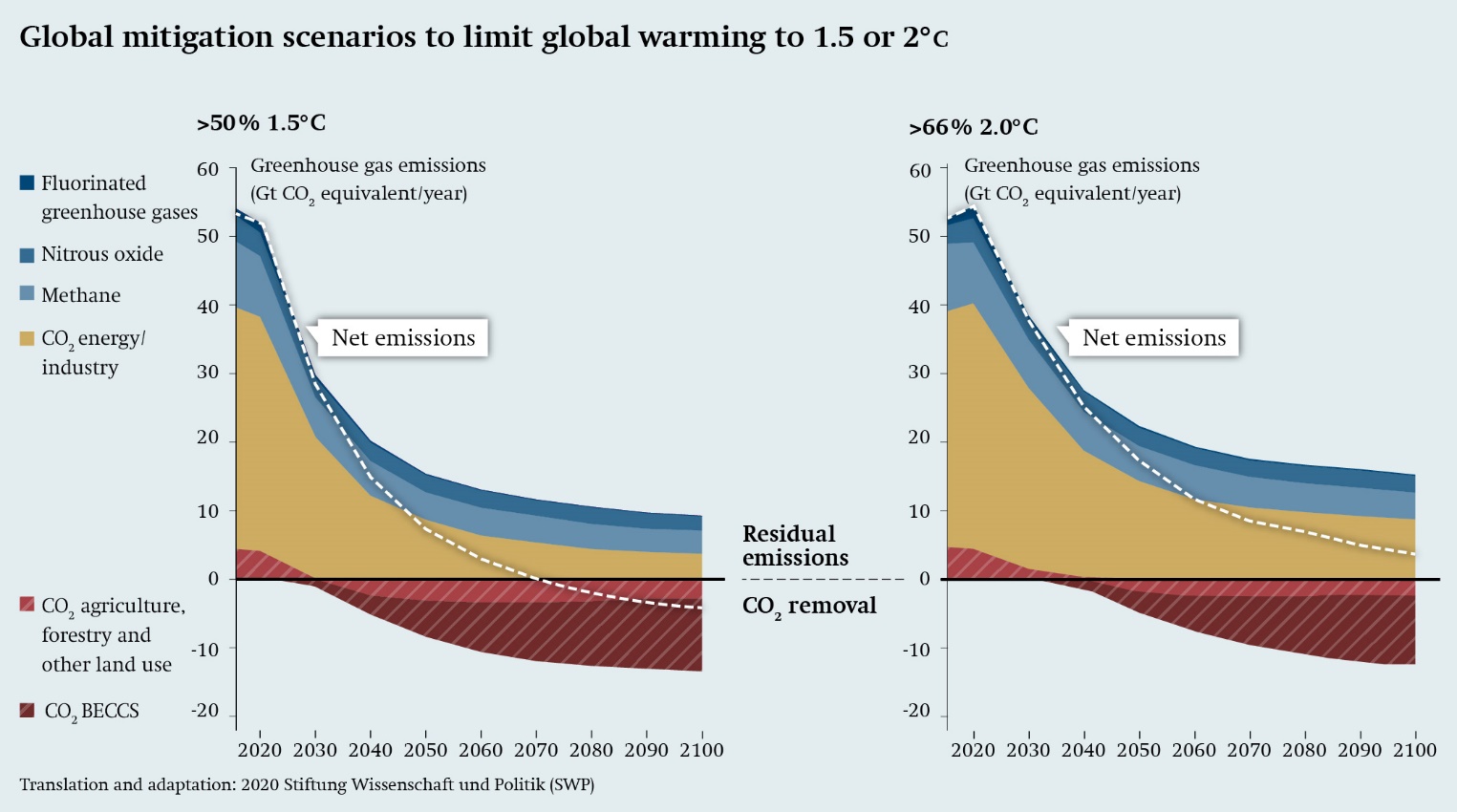
Unconventional Mitigation Swp
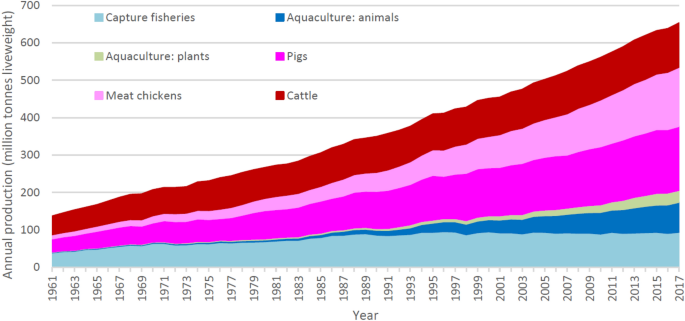
Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Global Aquaculture Scientific Reports

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Greenhouse Gases Bioninja

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Economic Performance Greenhouse Gas Emissions Environmental Management And Supply Chains In India A Comparison With Japan Intechopen

Carbon Cycle Definition Steps And Examples Biology Dictionary

Team Braunschweig Project Content 14 Igem Org

Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Alternative Futures Of Deforestation And Agricultural Management In The Southern Amazon Pnas

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change

Greenhouse Effect Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
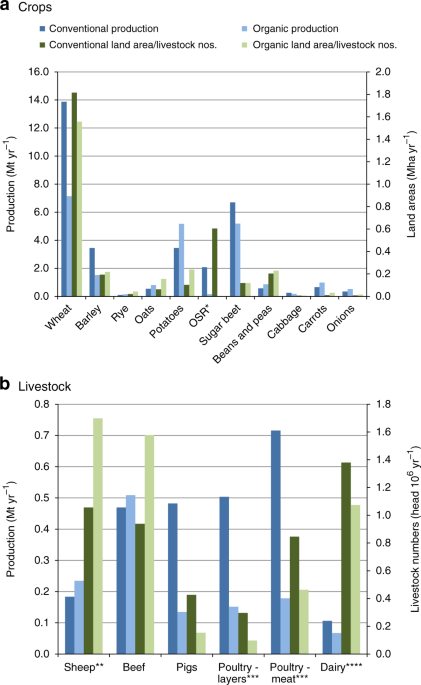
The Greenhouse Gas Impacts Of Converting Food Production In England And Wales To Organic Methods Nature Communications

Climate Change Biology 101 With Pruett At University Of Chicago Studyblue

Iso 1 18 En Greenhouse Gases Part 1 Specification With Guidance At The Organization Level For Quantification And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Removals

Climate For Peace Toolkit By Sci Service Civil International Issuu

Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids

Robust Paths To Net Greenhouse Gas Mitigation And Negative Emissions Via Advanced Biofuels Pnas

File Nanchang No 2 Science 10 Biology 11
Http Www Searchanddiscovery Com Documents 09 trenberth Ndx Trenberth Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsacfivl5yiym1z15qpgc24i5ya0kio Ipgu6d Zzdrtujy0gne Usqp Cau

Global Warming And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Definition Of The Greenhouse Effect

Greenhouse Topics Tree Nation Forestry Knowledge Database
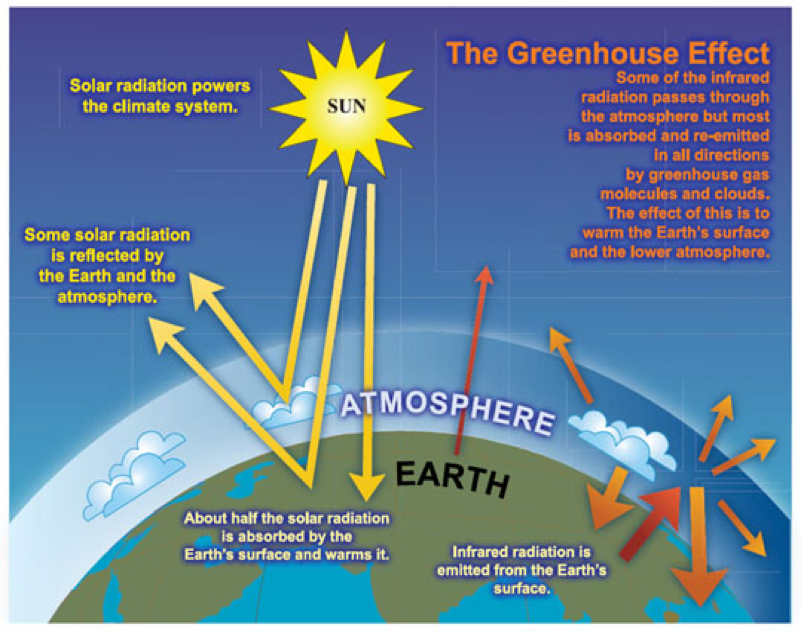
Greenhouse Gas Reduction

Greenhouse Gas New World Encyclopedia
Environment For Kids Global Warming
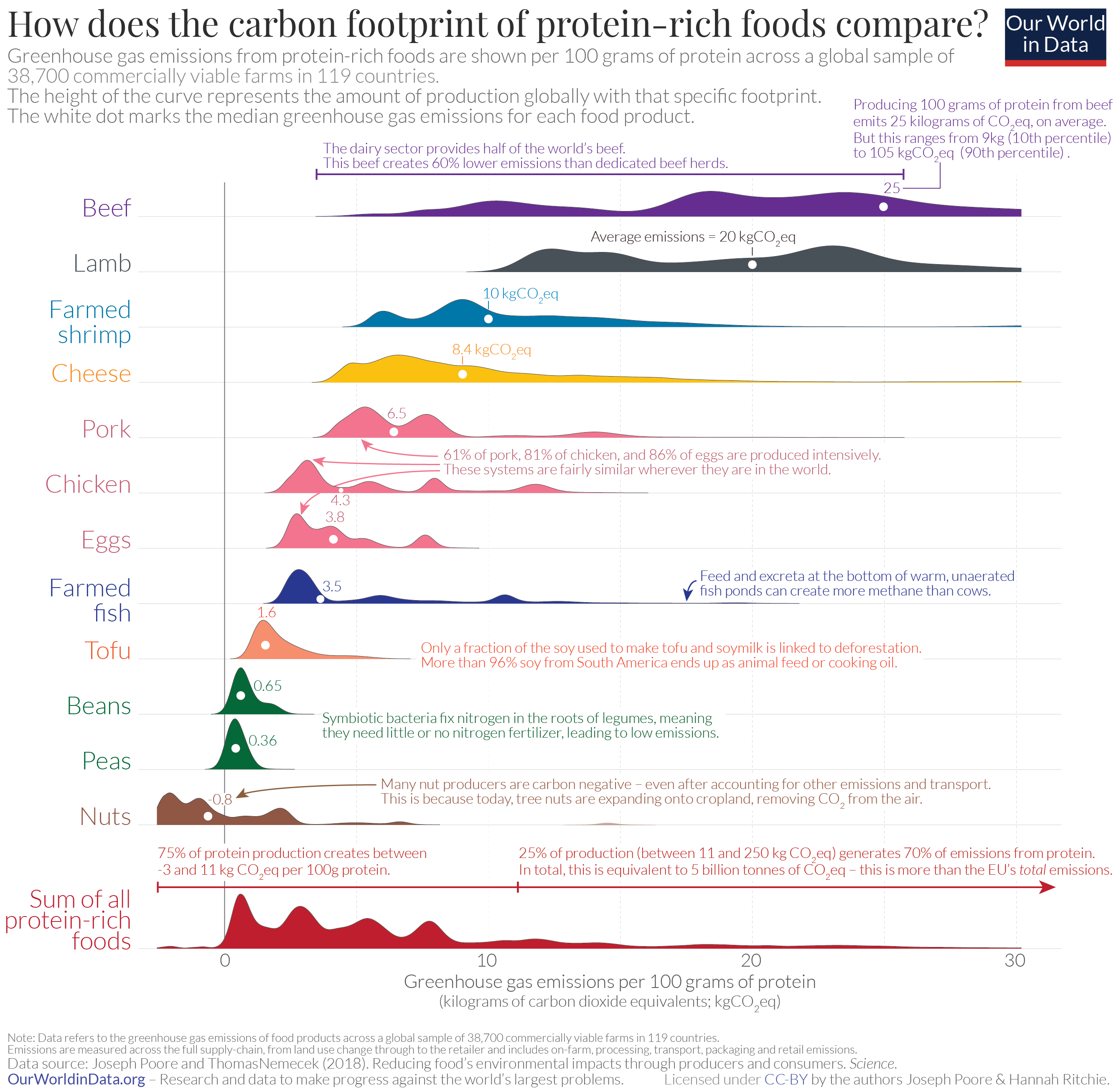
Less Meat Is Nearly Always Better Than Sustainable Meat To Reduce Your Carbon Footprint Our World In Data
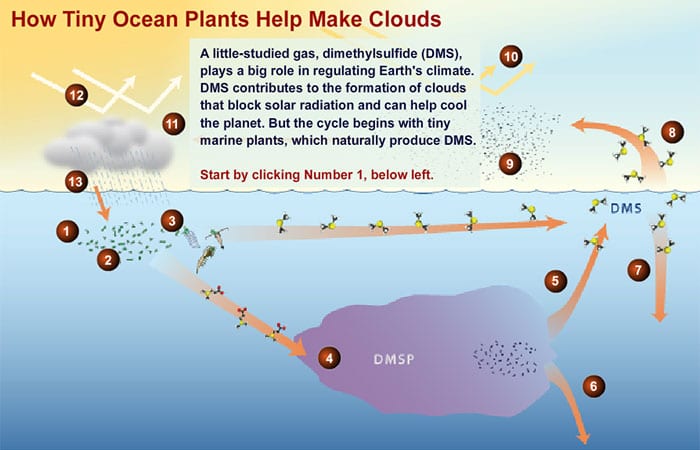
Dms The Climate Gas You Ve Never Heard Of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution

Greenhouse Effect

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
2
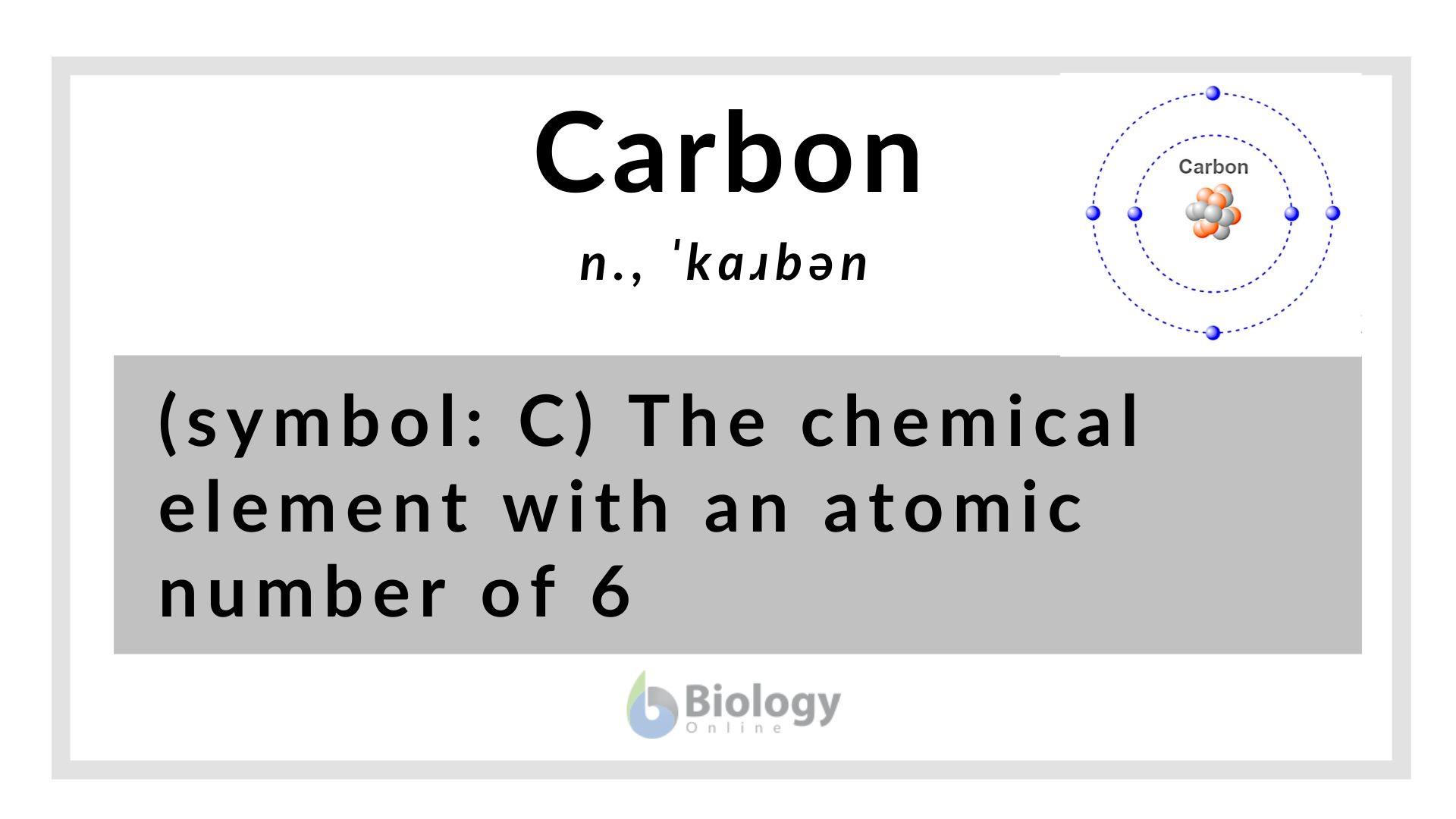
Carbon Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary

6 Humans Affect Climate

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com
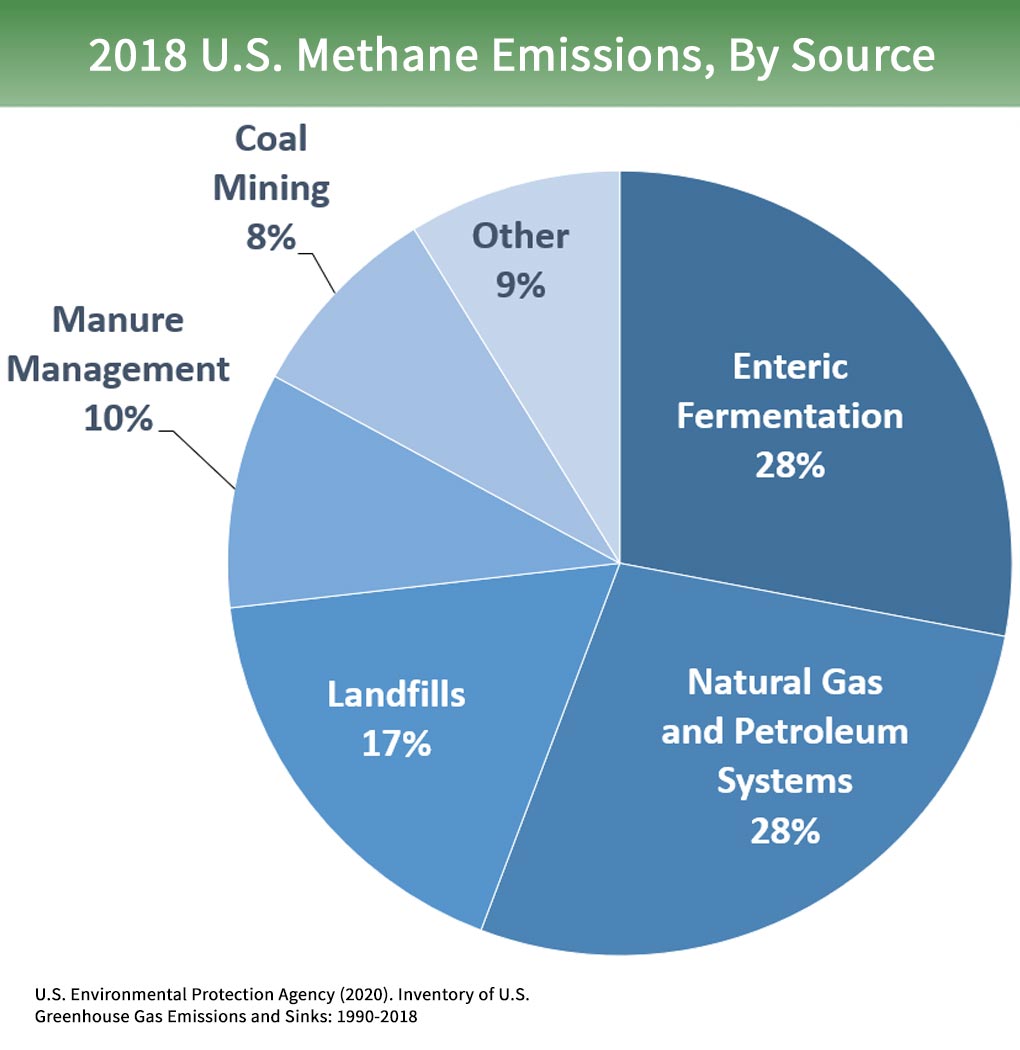
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Carbon Dioxide Controls Earth S Temperature

Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay

Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube

Greenhouse Gases Air Pollution Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download
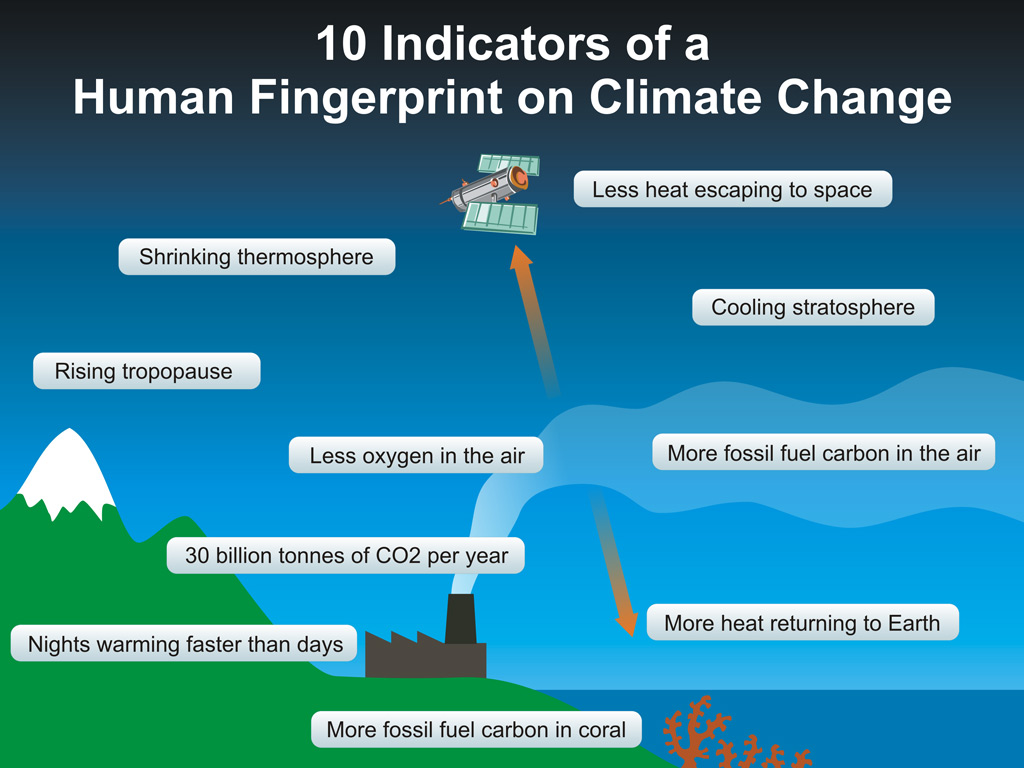
The Human Fingerprint In Global Warming
8 Life Cycle Assessment Of Carbon Utilization Gaseous Carbon Waste Streams Utilization Status And Research Needs The National Academies Press
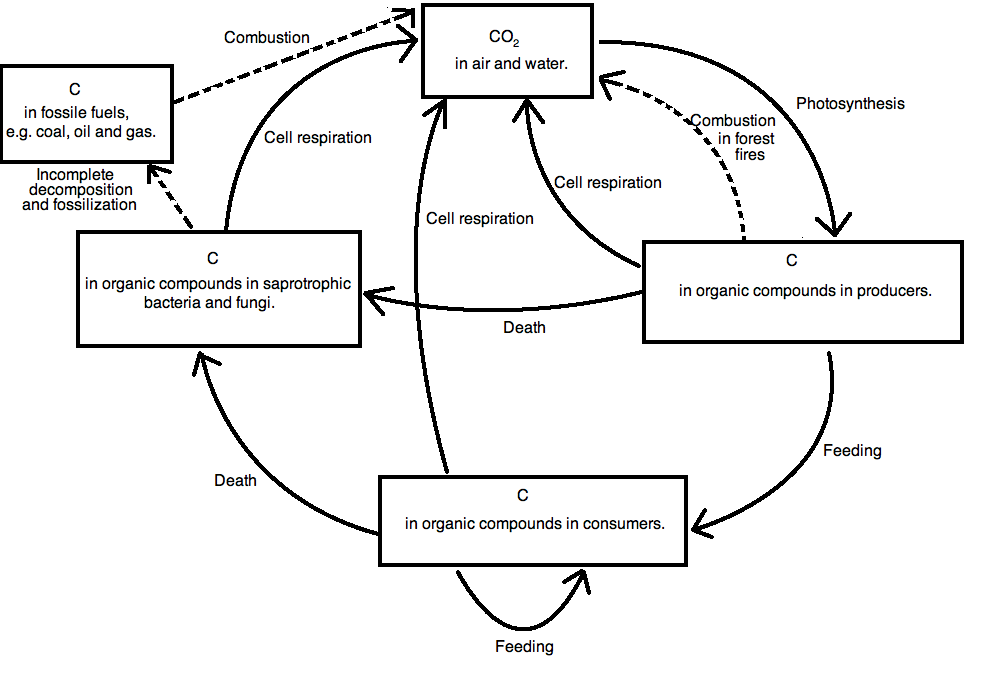
Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect

What Is Carbon Neutral Carbon Free Boston
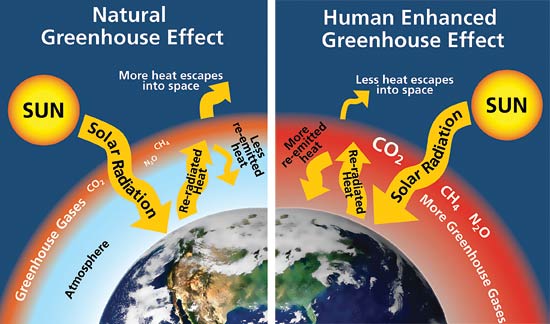
Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions

Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences

Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society

The Archean Atmosphere Science Advances

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
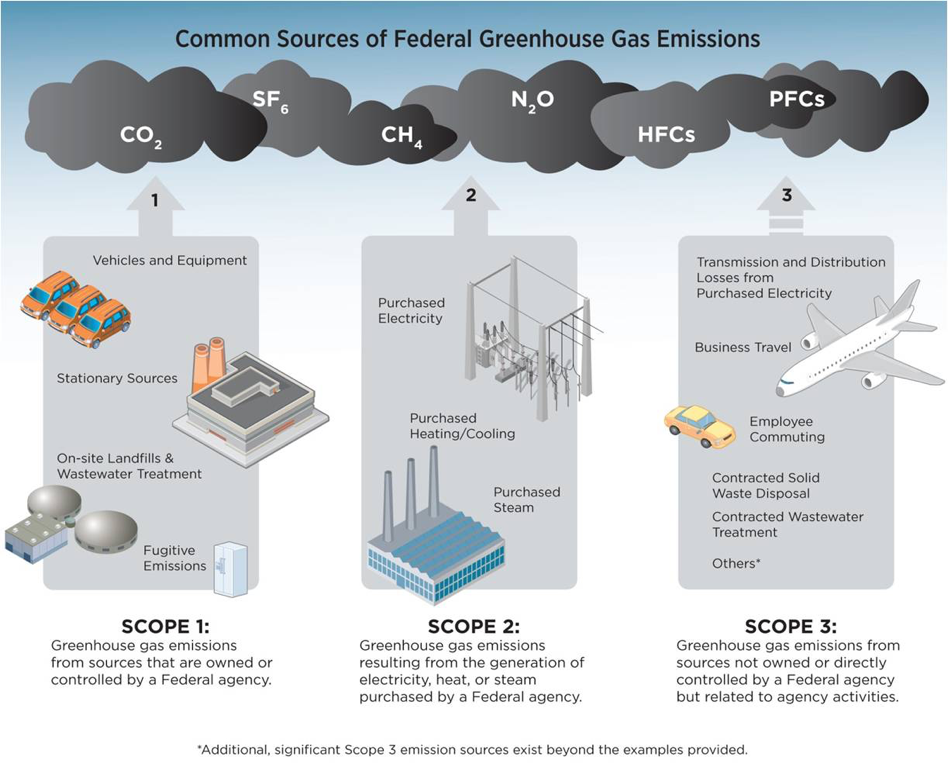
Greenhouse Gas Reduction

Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects

Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions Internationale Klimaschutzinitiative Iki

Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Definition Greenhouse Effect Define Greenhouse Effect Gases Greenhouse Effect In Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq4vuhxg58siiojyhrbz5zz9an1gpkudyxaxrotok Wpysb0oks Usqp Cau
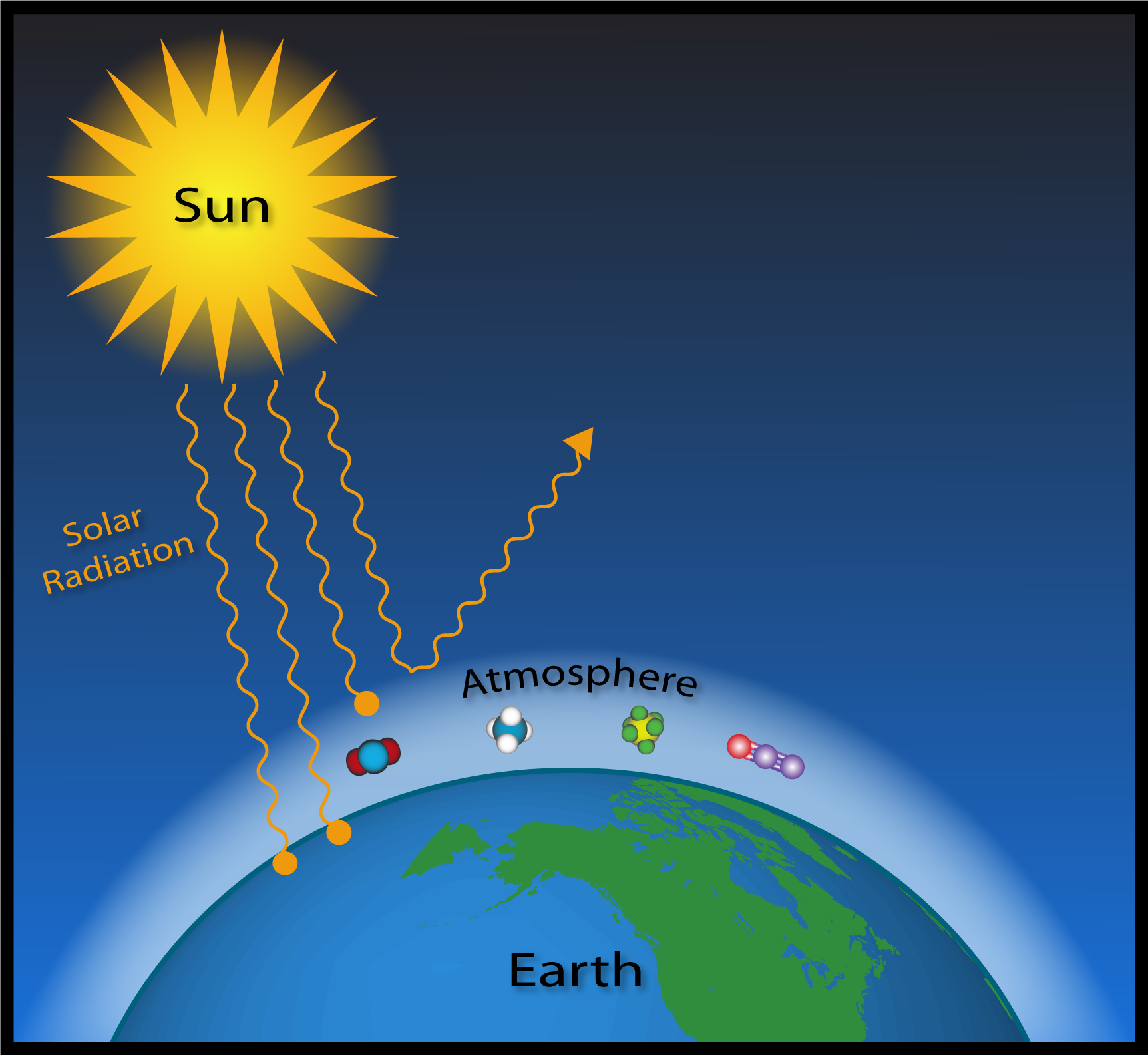
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions

Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society



