Greenhouse Gas Effect Model
The model is an instructional "toy model," meaning it strips the process down to its essential elements so that the basic ideas are easy to convey.
Greenhouse gas effect model. Gases are not the only contributors to the greenhouse effect:. A different analogy is the atmosphere acting like a blanket. Two identical glass jars 4 cups cold water 10 ice cubes.
GreenSTEP Greenhouse Gas Statewide Transportation Emissions Planning Mode l (VisionEval family) GREET GHG, Regulated Emissions, and Energy Use in Transportation Model. Greenhouse effect, Greenhouse gases, Increase of carbon dioxide, Global temperature rising, Effect of global warming, Wa. Plant-wide control strategy.
HB House Bill. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Today, the surface of Venus is hot enough to melt lead.
HCS Highway Capacity Software. People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors:. This makes a great homework sheet or in-class review.
In its atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder on average than it is now. What happens when you add clouds?. The farming systems included:.
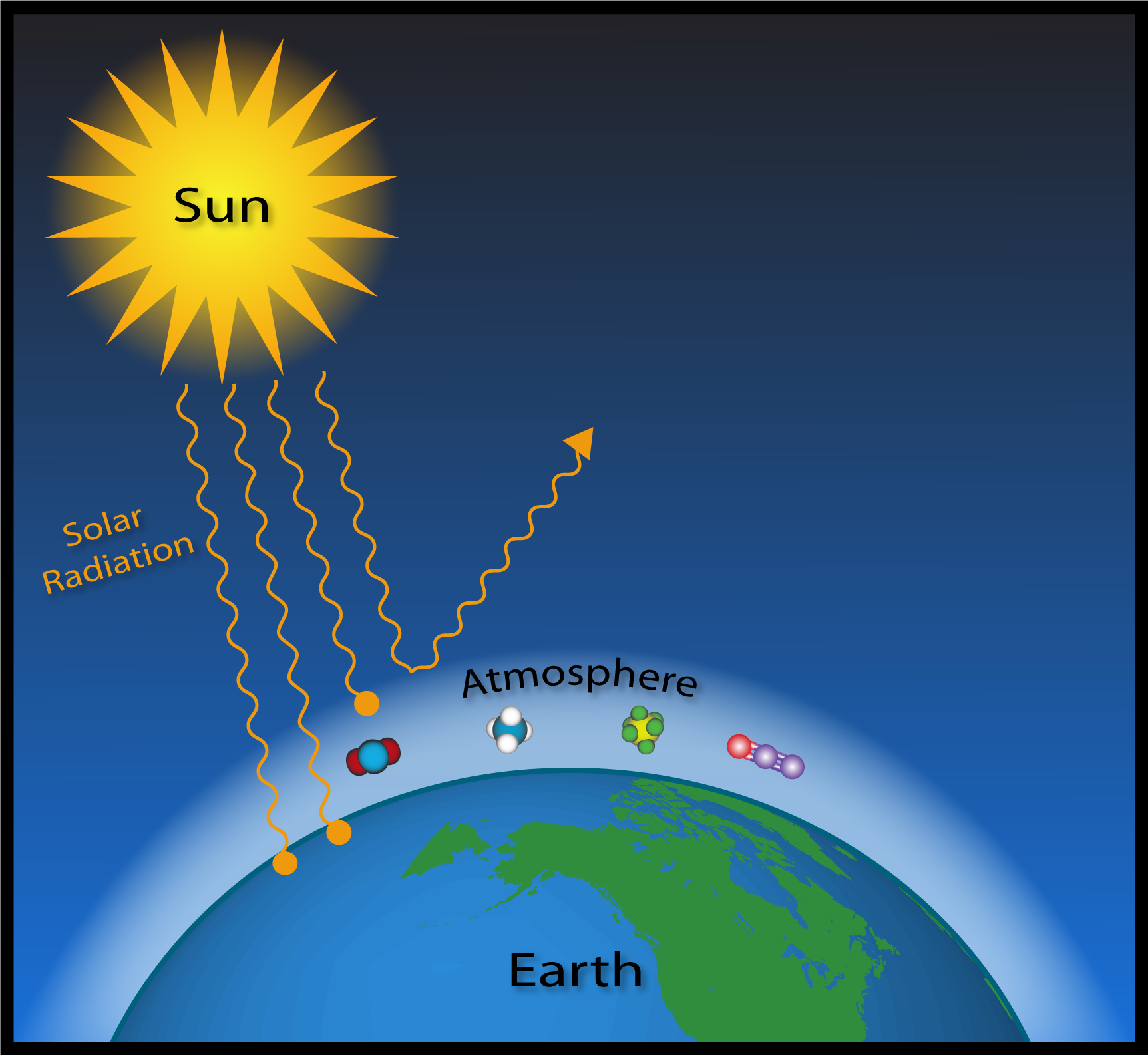
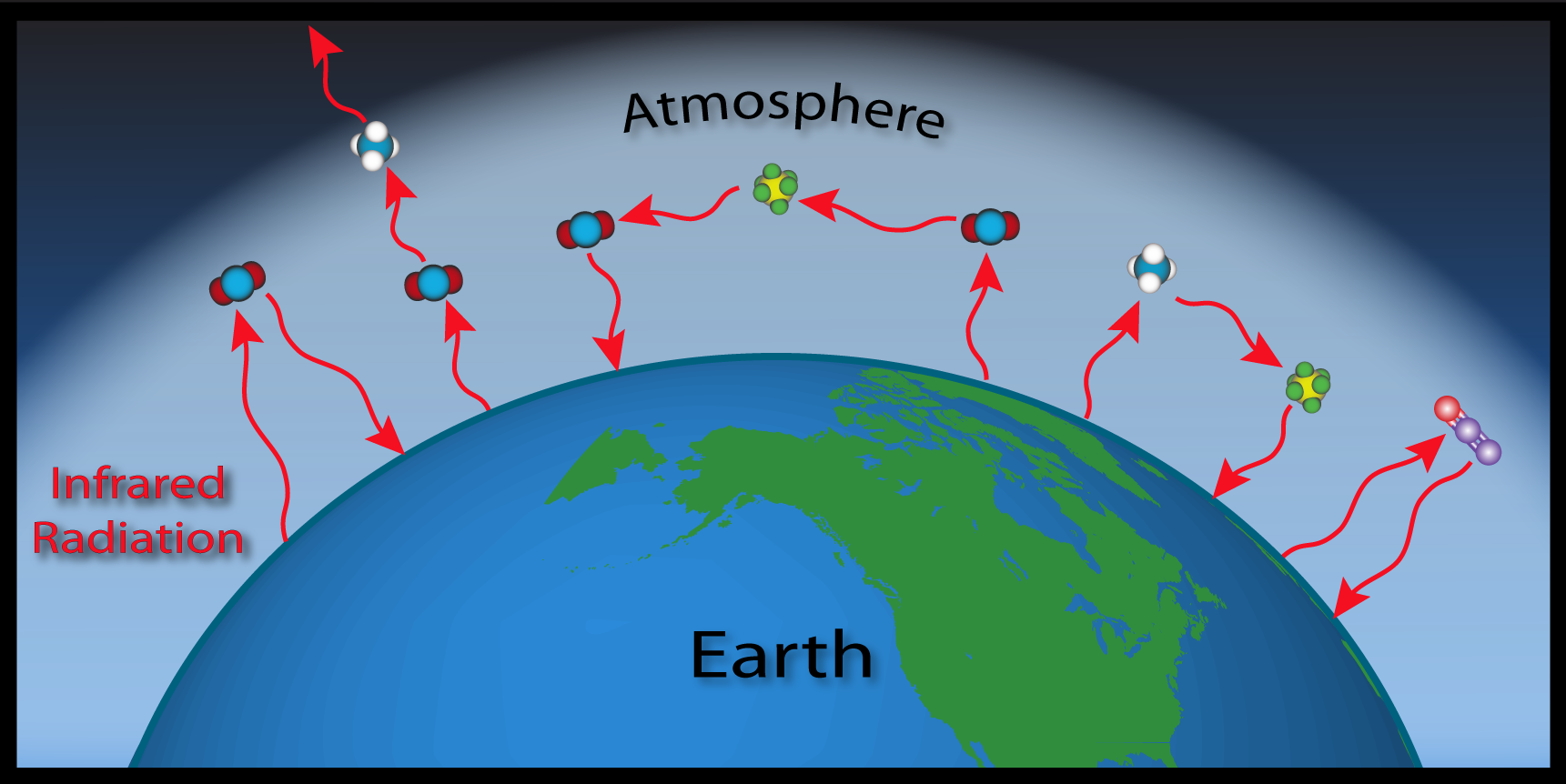
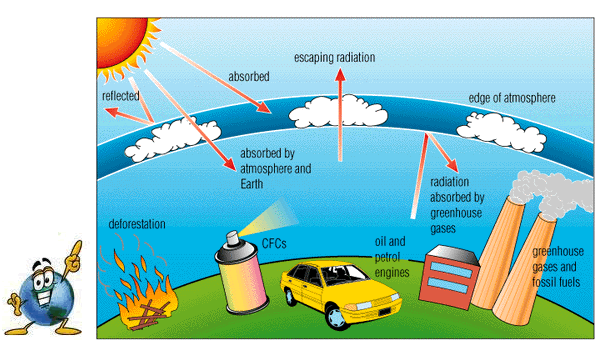
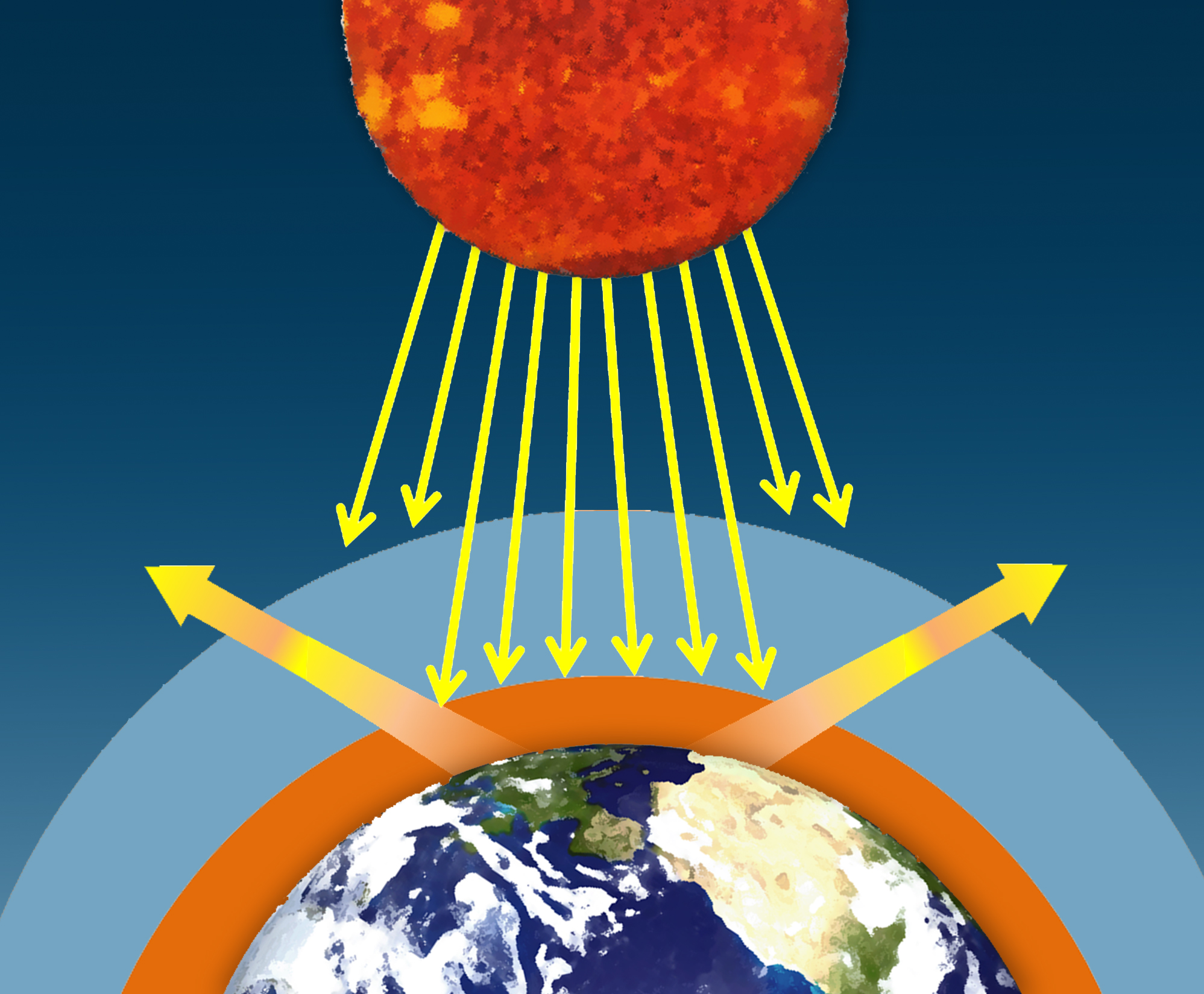
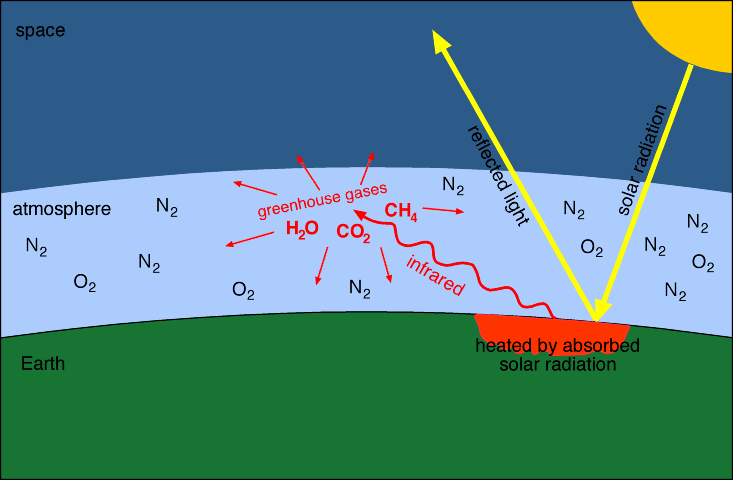
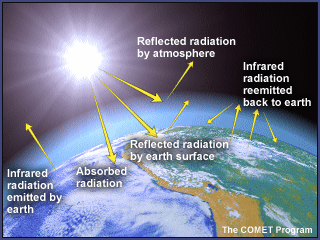
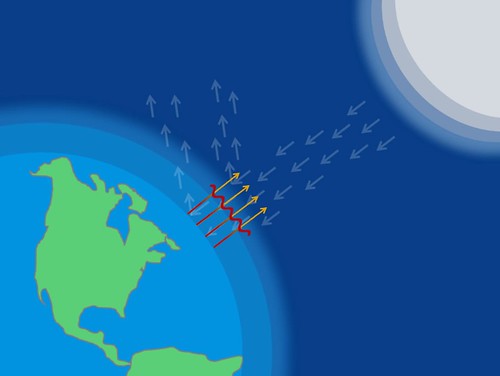
Some gases, when present in the atmosphere, absorb that reflected energy and redirect it back to Earth as heat. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer. The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be.
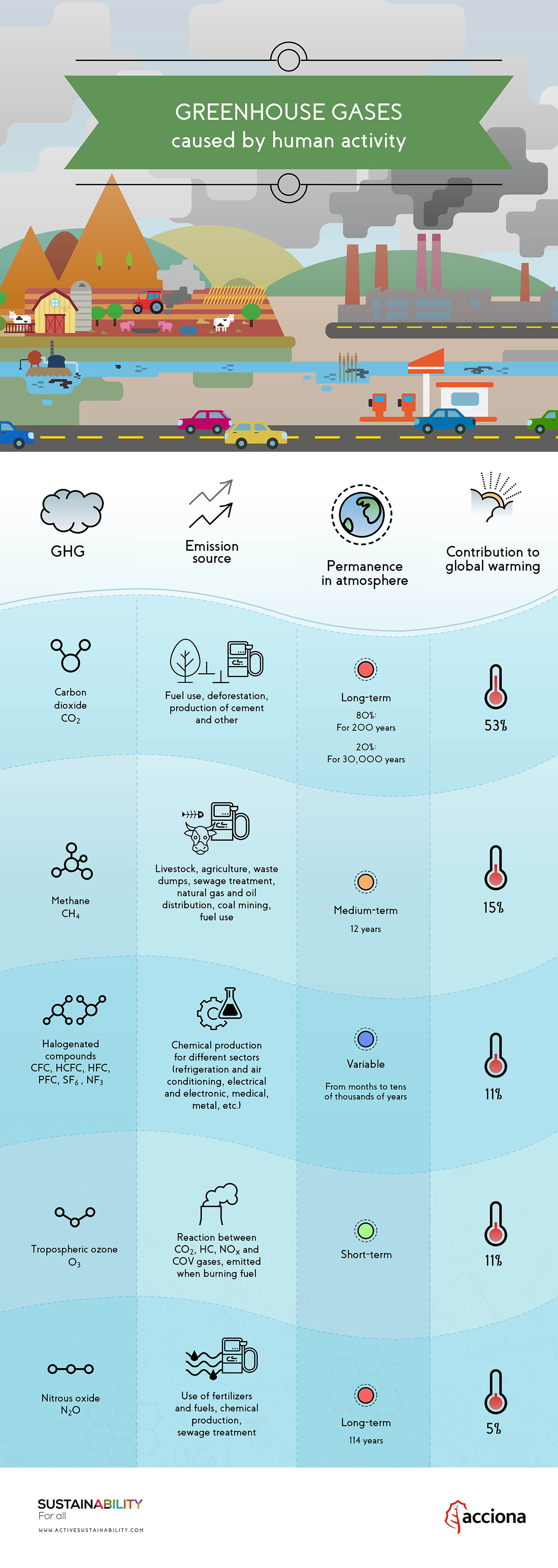
A comparison of our various models indicates that the surface changes are driven to a large extent by the effect of the greenhouse gases on the stratosphere. HPMS Highway Performance Monitoring System. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases.
The clear effect of the greenhouse gases is the stable heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface, thus, global warming. The gases formed by the burning, such as carbon dioxide, are building up in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer.
The greenhouse effect can be illustrated with an idealized planet. The Greenhouse effect explained :. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth’s average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. This page presents a simple physical model of the greenhouse effect that demonstrates how the blanketing effect of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can elevate the surface temperature of a planet.
Yet its production of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions remains unclear. Then compare to the effect of glass panes. The Earth's surface absorb the sunlight’s energy.
This worksheet has 22 Earth Science Regents questions about the the greenhouse effect and global warming. Doing so would involve overcoming the natural greenhouse effect. This is not an official version of GEM and it cannot be used for compliance with EPA emission standards.
(To a lesser extent, surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap. The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experiences because greenhouse gases trap energy from the sun. Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F).
Finally, they revise their model of the greenhouse effect using their data analysis and an. 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time. This Video covers :.
In this idealized model, the greenhouse gases cause the surface of the planet to be warmer than it would be without them, in order for the required amount of heat energy finally to be radiated out into space from the top of the atmosphere. EPA is releasing the following version of the model (GEM_P2V3.5) which incorporates the revisions being considered. Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes.
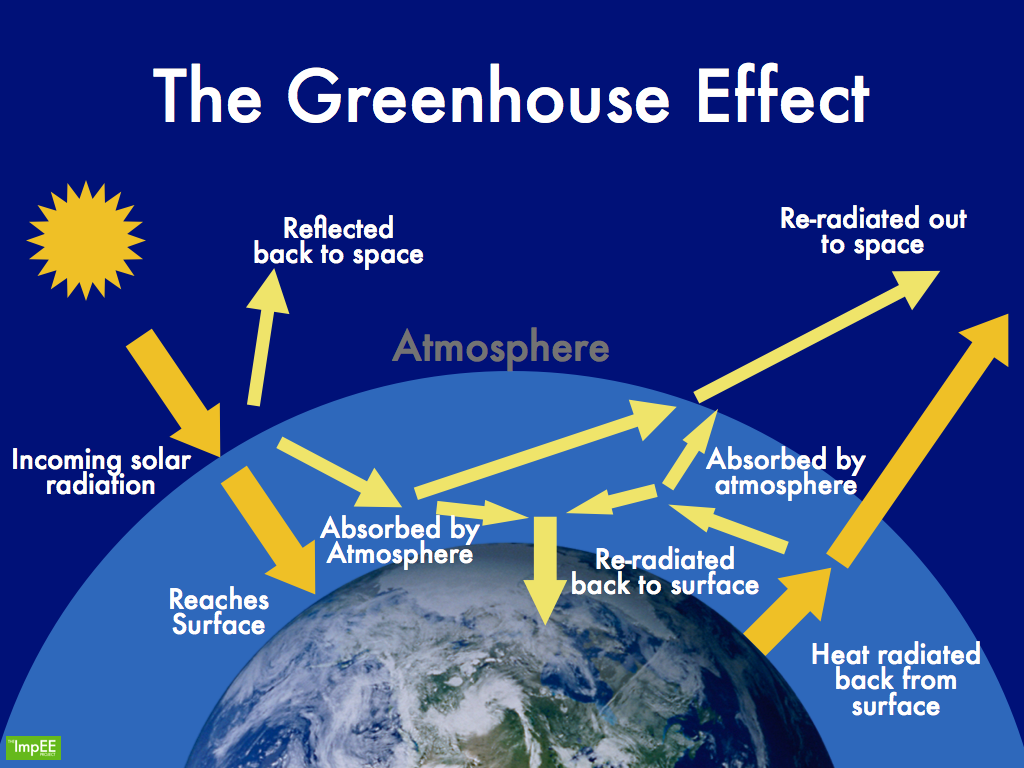
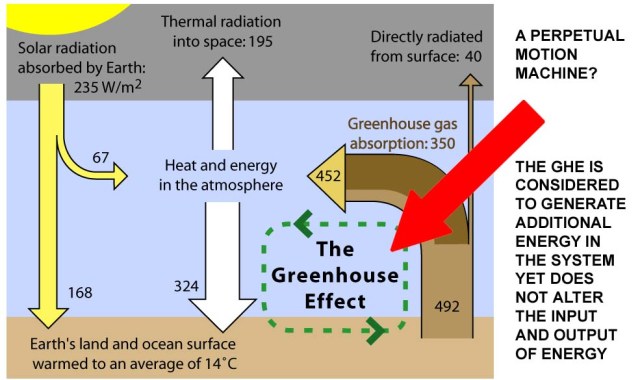
Solve for T T = 255K (-18° C) Known T = +15° C, 33° C higher than model Why:. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. Recent research into greenhouse gas emission scenarios provides guidance on what will need to happen to stabilise Earth’s.
However, the way the Earth and its atmosphere work to stay warm is different from the way a greenhouse works, so the term “greenhouse effect” is a bit misleading. - What is Global Warming?. However, an enhanced greenhouse effect due to human activity, such as burning fossil fuels for energy, can be detrimental to Earth's climate and ecology.
Absorbs outgoing radiation) solar Earth radiation absorbed reflected reradiated History Early atmosphere of earth ~1000 x more CO2 Enabled development of life 6 CO2+ 6 H2O C6H12O6+ 6 O2. Black carbon, otherwise known as soot, as well as some other particulate matter can also play a role. Here, a randomized plot field experiment was performed to study the GHG emissions for various farming systems during the rice growing season.
This is known as a runaway greenhouse effect. The Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases (CCGG) research area operates the Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network, measuring the atmospheric distribution and trends of the three main long-term drivers of climate change, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O), as well as carbon monoxide (CO) which is an important indicator of air pollution. Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today.
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth’s atmosphere. Jul 29, 14 - Explore Jane Parker's board "Greenhouse Gases" on Pinterest. Water vapor is known to be Earth’s most abundant greenhouse gas, but the extent of its contribution to global warming has been debated.
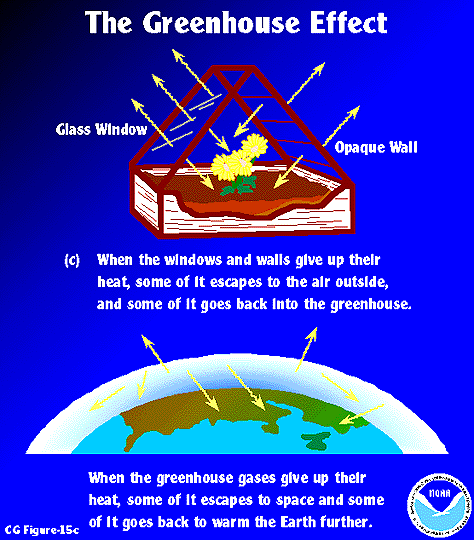
But such materials have even shorter residence times, typically just days or weeks, as they tend to be flushed out of the air by the next rainfall. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Model (GEM) User Guide (PDF) (46 pp, 1.5 MB, March , EPA-4-B--019, About PDF). The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them.
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which radiation from the sun is absorbed and reflected by the Earth's surface;. The result, experts believe, is that the Earth heating up and undergoing global warming.
HCM Highway Capacity Manual. Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century. The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere.
Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such. How do greenhouse gases affect the climate?. Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface.
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. The greenhouse effect works like this:. These greenhouse gases keep the surface of the Earth approximately 60F warmer than we would expect without these gases present.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. While Earth's surface has warmed over recent decades, the stratosphere has cooled and stratospheric winds have increased. As you might expect from the name.
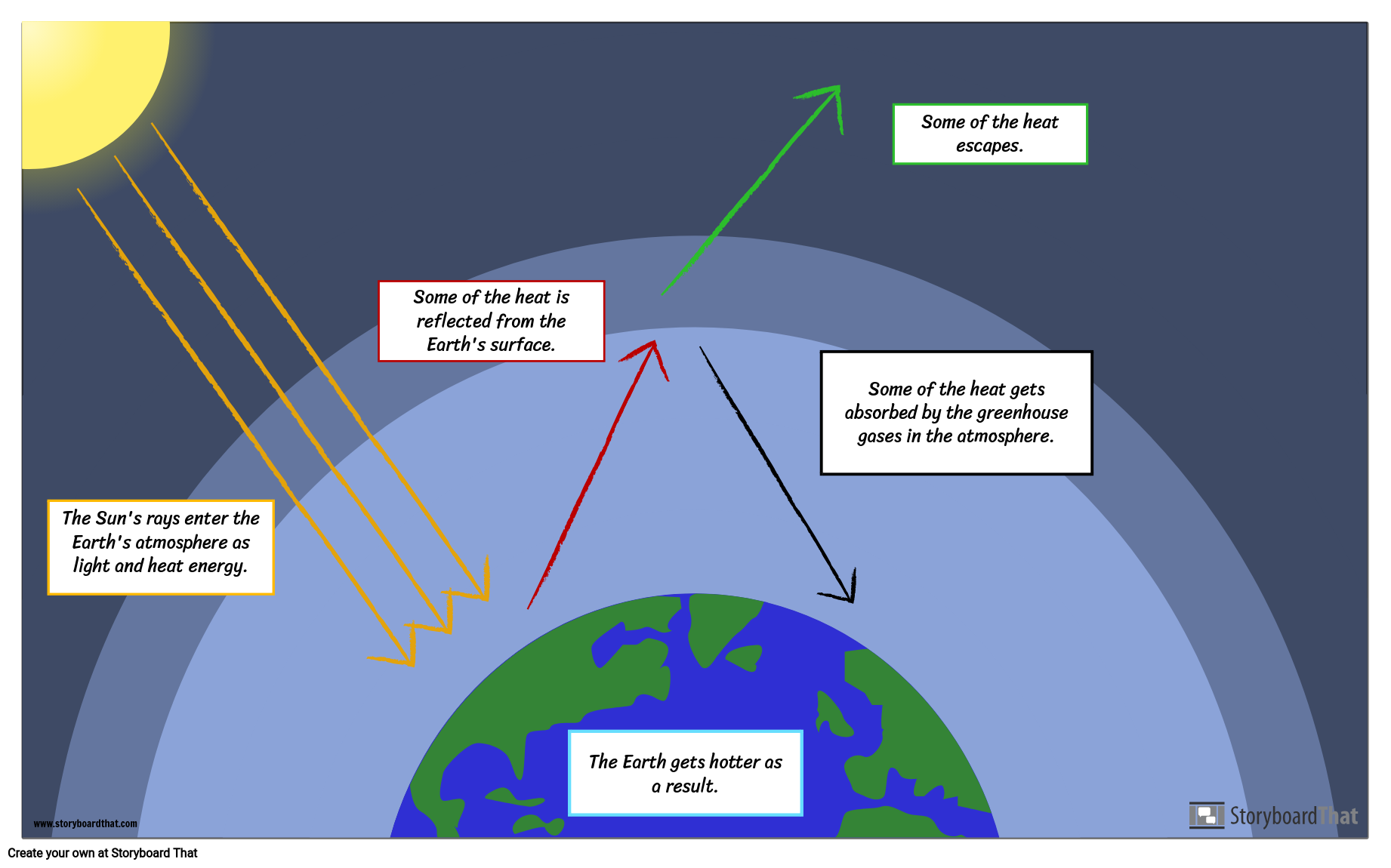
Greenhouse Effect (Atmosphere transmits incoming radiation;. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides. Some of the reflected radiation makes its way back through the atmosphere, and some is absorbed by greenhouse gas molecules that then re-emit the radiation in all directions in the atmosphere warming the surface of the Earth.
Absorption coefficients calculated using a line-by-line radiative transfer model (Francis and Edwards, 07) with the HITRAN04 spectral database for water vapour (black curve) and carbon. In computer-based models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time. Integrated rice-frog farming (IRFF), as a mode of ecological farming, is fundamental in realizing sustainable development in agriculture.
They act like greenhouse glass. The effect of no- and reduced tillage (NT/RT) on greenhouse gas (GHG) emission was highly variable and may depend on other agronomy practices. See more ideas about Greenhouse gases, Gas, Greenhouse.
Absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the. Energy from sunlight is also the source of the warmth on Earth, because the atmosphere is pretty transparent to sunlight. One of a suite of online climate interactive simulations, this Greenhouse Gas Simulator uses the bathtub model to demonstrate how atmospheric concentrations of CO2 will continue to rise unless they are lowered to match the amount of CO2 that can be removed through natural processes.
Once absorbed, this energy is sent back into the atmosphere. The greenhouse effect, combined with increasing levels of greenhouse gases and the resulting global warming, is expected to have profound implications, according to the near-universal consensus of. Towards a benchmark simulation model for.
Greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which thermal radiation from earth’s surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions. These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Greenhouse gas is water vapour, with car-bon dioxide the next most important.
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions have gained international attention due to their effect on global climate.There are many sources of GHG emissions, with agriculture estimated to contribute about 11% of all global emissions (Smith et al., 14) and 8.4% of US emissions ().Livestock have received extra attention for their contribution to GHG emissions along with other environmental. Using recent NASA satellite data, researchers have estimated more precisely than ever the heat-trapping effect of water in the air, validating the role of the gas as a critical component of climate change. ICE Infrastructure Carbon Estimator.
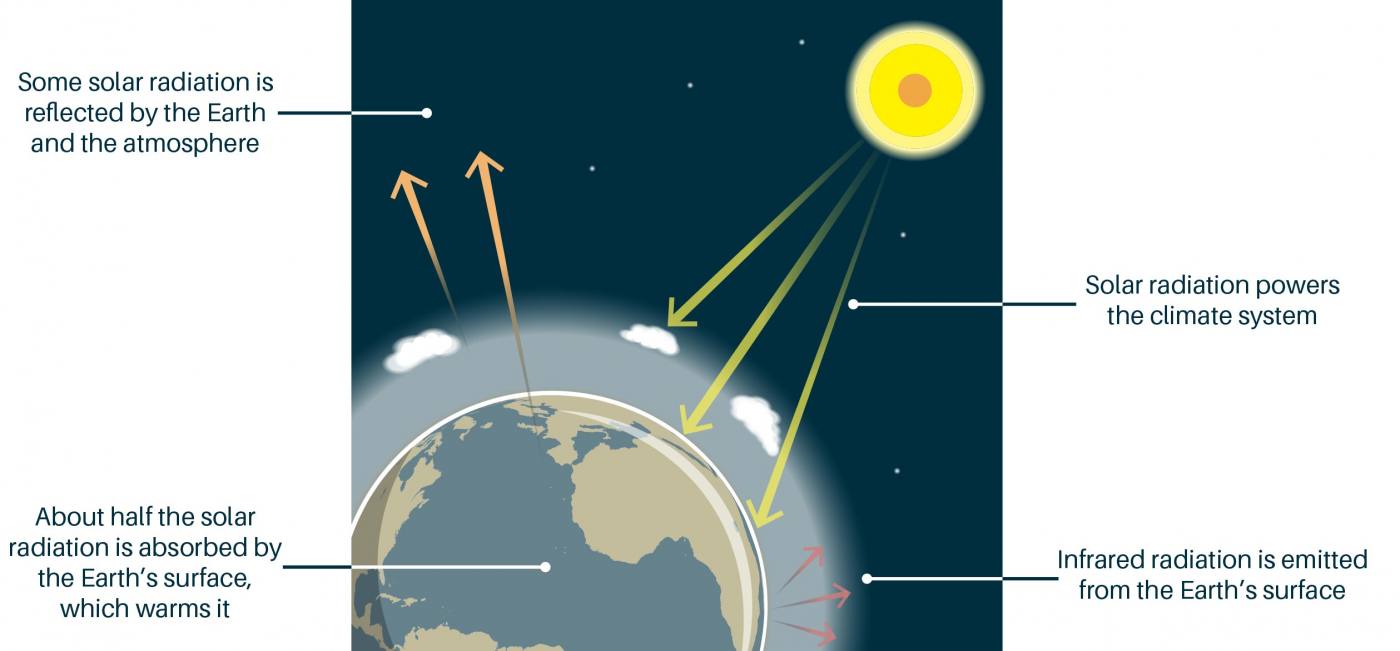
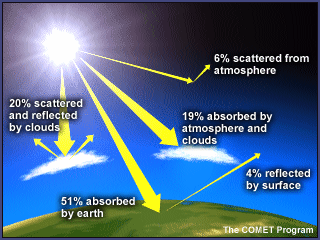
To lessen those long-term effects, many nations, communities, and individuals are taking action now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow global warming by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, increasing the use of renewable energy, expanding forests, and making lifestyle choices that help to sustain the environment. Use the "Greenhouse Gas Concentration" slider control to vary the amount of greenhouse gases;. A lot of the sun’s energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space.
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without. The greenhouse effect is a natural, integral part of the Earth that keeps our world warm enough to sustain life. The spectral properties of HO and CO are por-Figure 2.
Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?. Runaway greenhouse scenarios on Earth. - What is Green House.
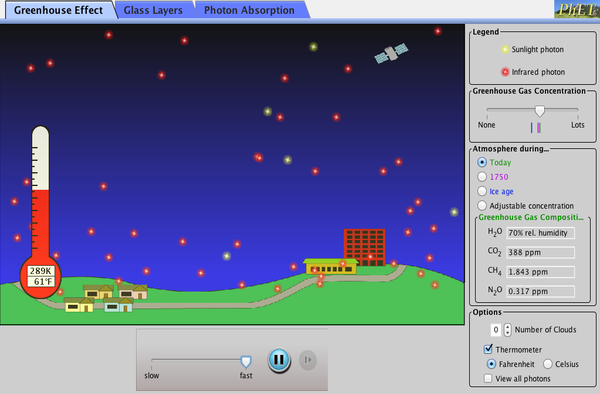
First, the sun’s energy enters the top of the atmosphere as shortwave radiation and makes its way down to the ground without reacting with the greenhouse gases. Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules. Check out our video on "Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming” by Letstute.
Observe the effect on temperature. Set the greenhouse gas concentration to "Lots", then observe the behaviors of the yellow photons representing sunlight and the red photons representing infrared emissions from Earth. Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, passing through the blanket of greenhouse gases.
How can you show the greenhouse effect?. In accordance with the Sustainable Development Goal 17 of improving global partnership for sustainable development, this study examined the effect of foreign direct investment inflows, economic development, and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions from 19 to 16 for the top five emitters of greenhouse gas emissions from fuel combustion in the developing countries, namely;. Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect.
Could continued warming on Earth cause the super greenhouse effect in these tropical regions to “run away” as it might have occurred on Venus?. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to live. Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet.
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Dontpassgas What Is The Greenhouse Effect

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
Greenhouse Gas Effect Model のギャラリー

Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram

The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia

Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram

Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
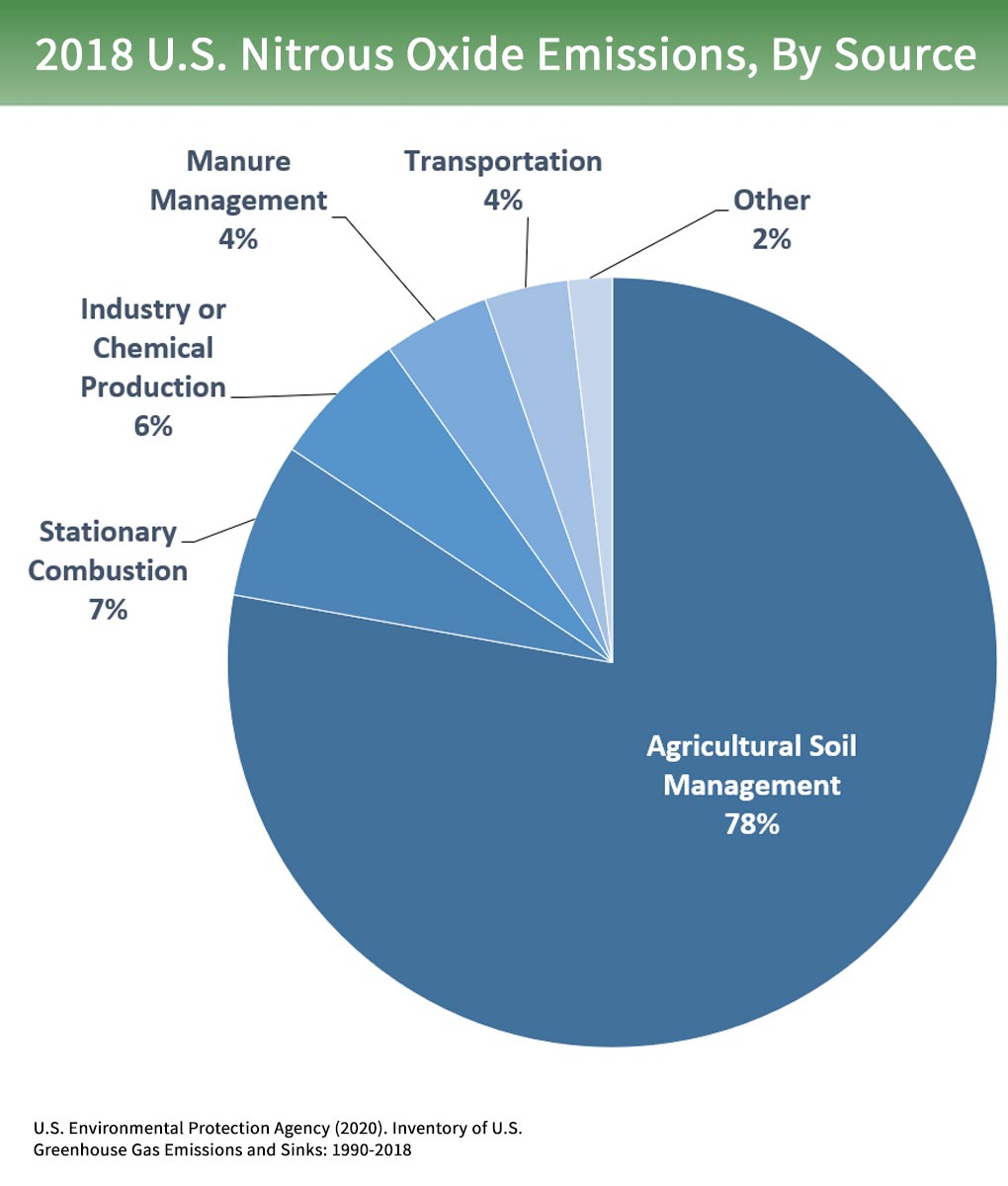
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqdqn3hrtggpwa2yxdsgbpthcktyf1idgi5cwnkwd Yzcnnkvbn Usqp Cau
Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Clip Art Free Clip Art On Clipart Library

The Greenhouse Effect World101

Visualizing The Greenhouse Effect A Physical Analogy Watts Up With That

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids

The Greenhouse Effect Explained

Ecology Lab The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Teacher Preparation Lab Activities

Greenhouse Effect Video For Kids The Greenhouse Effect Youtube
Climate Change Mitigation Wikipedia

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
What To Do At Home To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Journal Of Wild Culture
Iexfwtfp2g7snm

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Heat Phet Interactive Simulations
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate

Misconception Monday Is Greenhouse Misleading National Center For Science Education
.png)
Greenhouse Effect Energy Education

Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
The Greenhouse Effect
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

2c Explore The Greenhouse Effect

Computer Models To Study Greenhouse Effect

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Effect Model School Project For Students Exhibition Models The4pillars Youtube

Modeling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Ngss Aligned Stem Tpt

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrkshs4yxsmfkaj 7o4ctqd2sjucsgee2fpvlscwmrhqroqc Usqp Cau
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

Climate Change Indicators Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
The Tragic Tautology Of The Greenhouse Gas Effect Johnosullivan

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Interactive Online Tool Teaches Users About Climate Change Usda
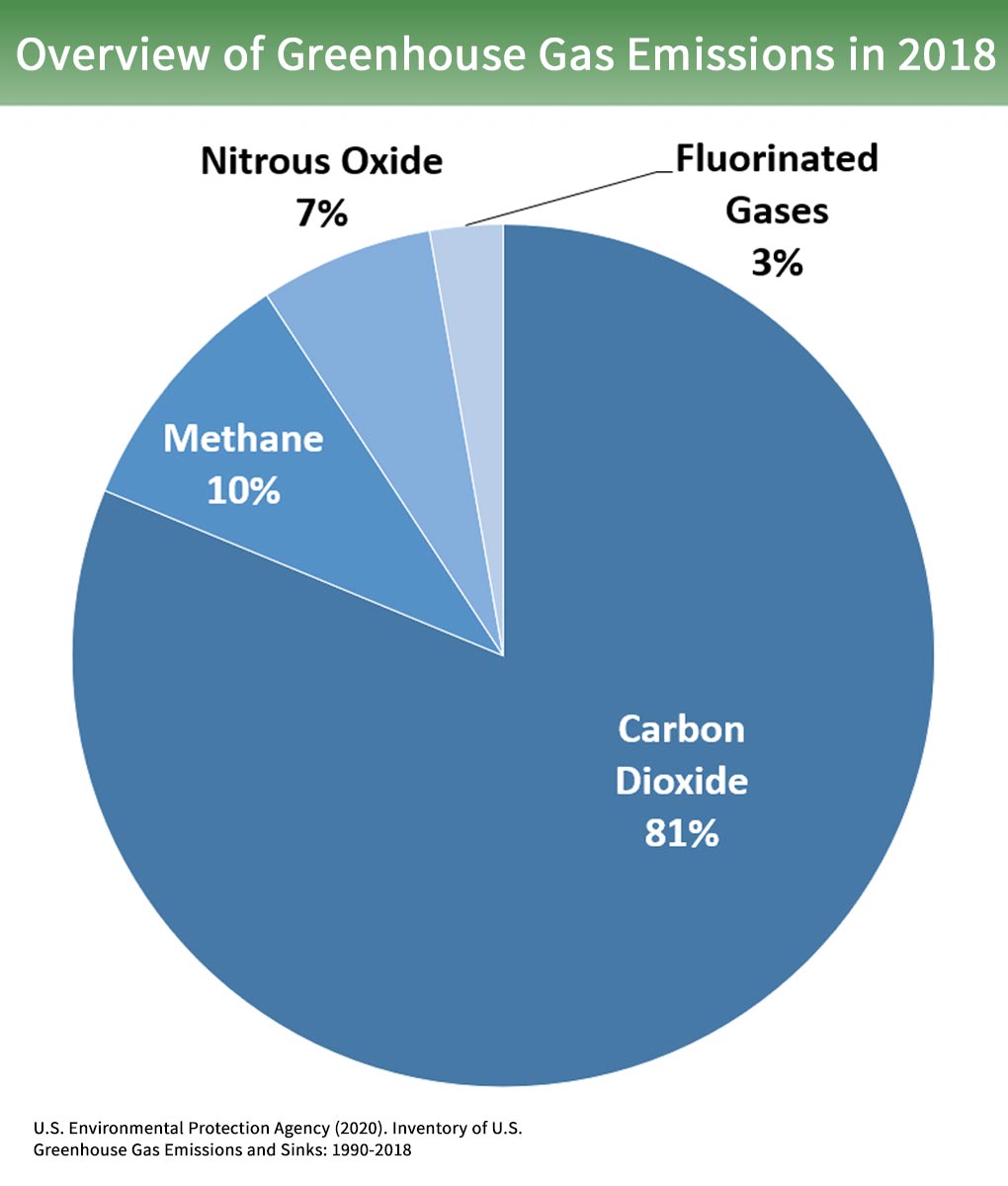
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Fis Effects Of Greenhouse Gases Youtube

Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Chemistry Byju S

What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
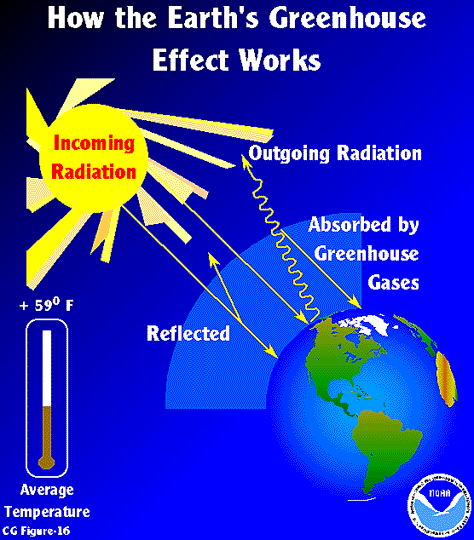
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
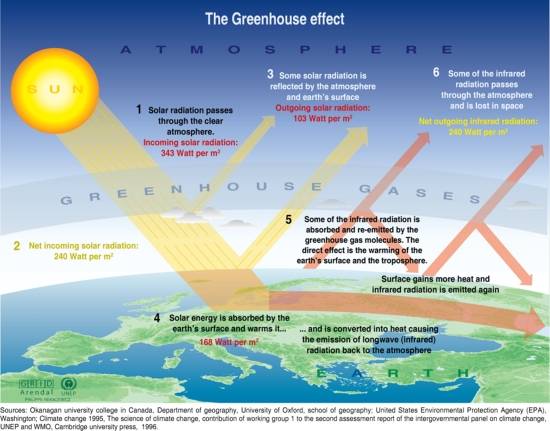
Greenhouse Gas

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect

The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses

The Greenhouse Effect World101
The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids

Does Nitrous Oxide N2o Has More Impact On The Climate And Human Health With Respect To Other Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gases Impact On Environment Iashe

Bacyosl8fihc5m

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

Solved 1 Greenhouse Gases And Temperature Simple Model Chegg Com

The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Science Classroom Poster Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Global Warming Project

Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood
1

Global Warming Impact On Greenhouse Gases Ag Decision Maker

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
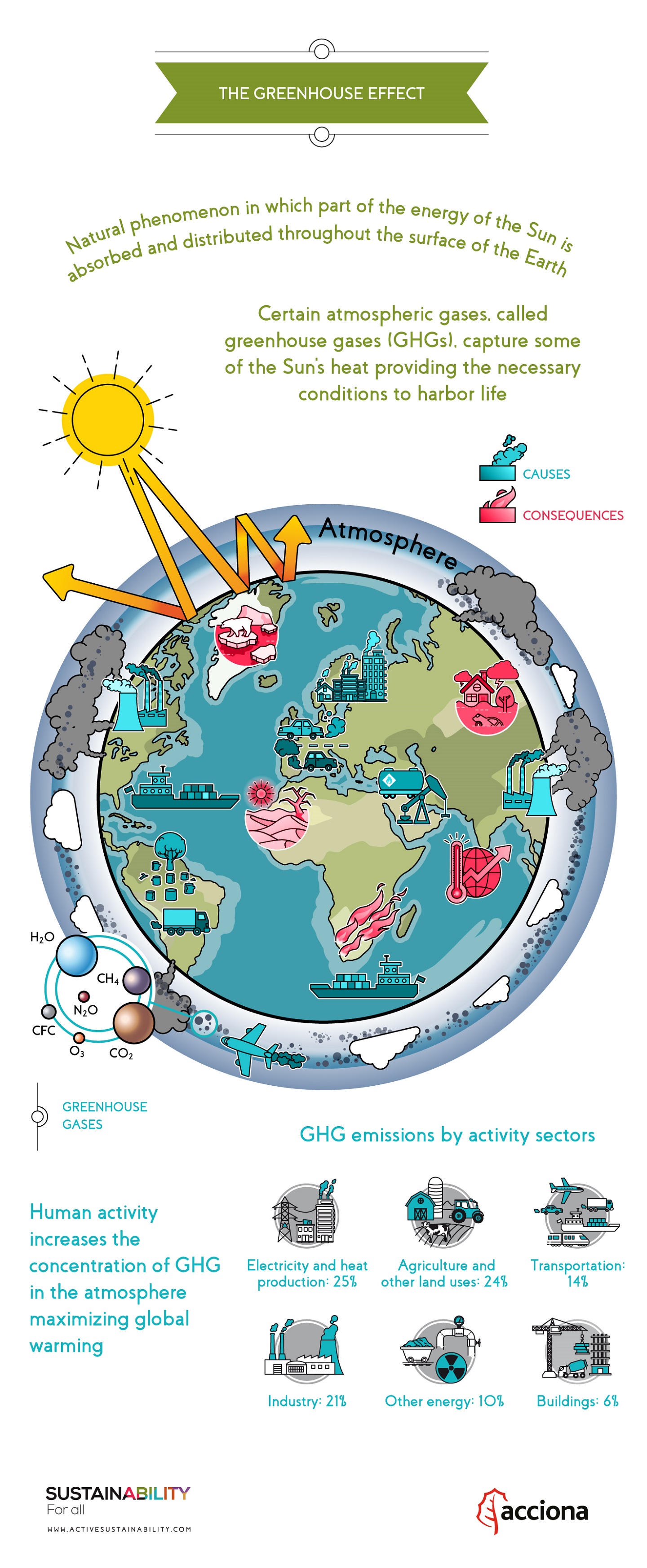
Reducing The Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases Springerlink

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases

Climate Change Mitigation Wikipedia
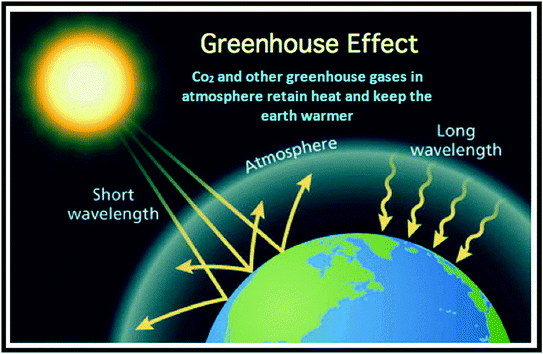
Untitled Document
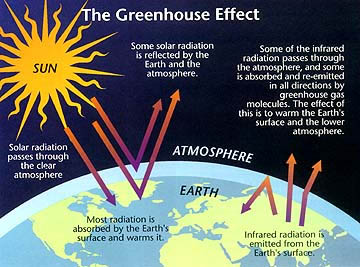
The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
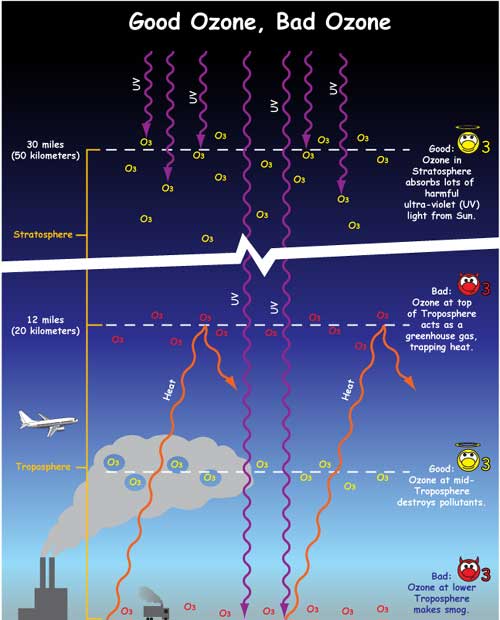
What Is The Greenhouse Effect

Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5440 Science Photo Library
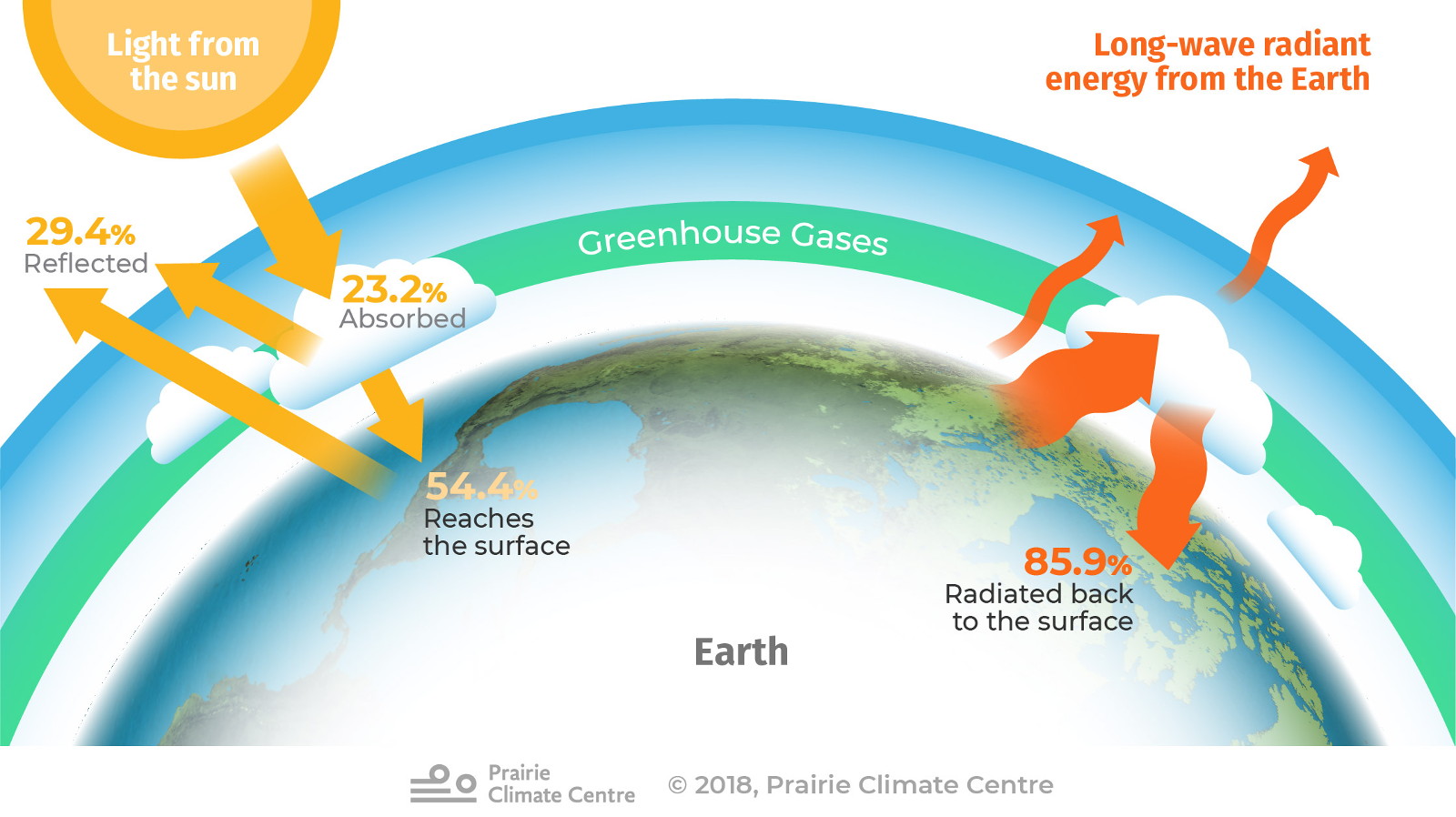
Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
3

Greenhouse Gases Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Visualizing The Greenhouse Effect A Physical Analogy Watts Up With That
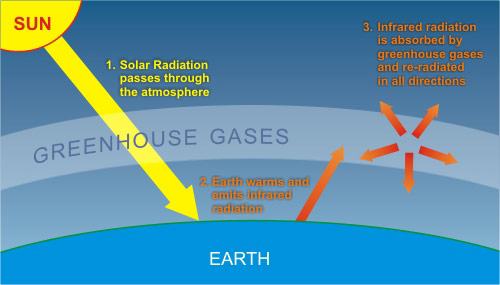
How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming

Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect

Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That Is A Great Way For Students To Combine I Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect Global Warming
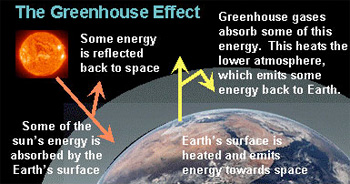
Volcanoes Greenhouse Gases And Temperature Change
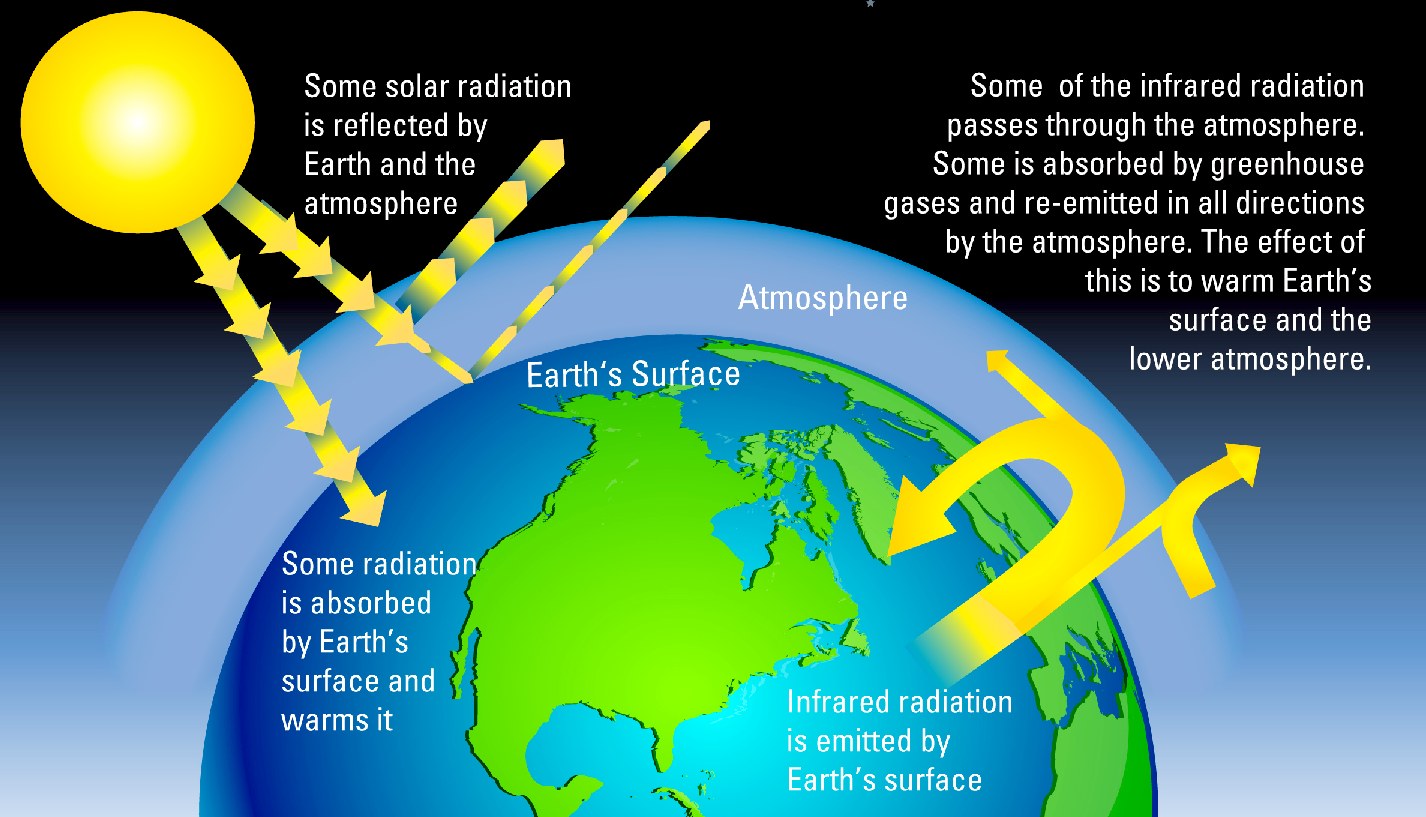
Greenhouse Gases
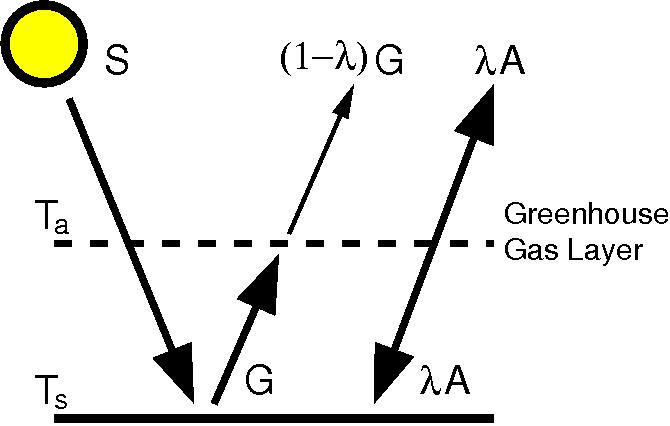
Learning From A Simple Model Realclimate
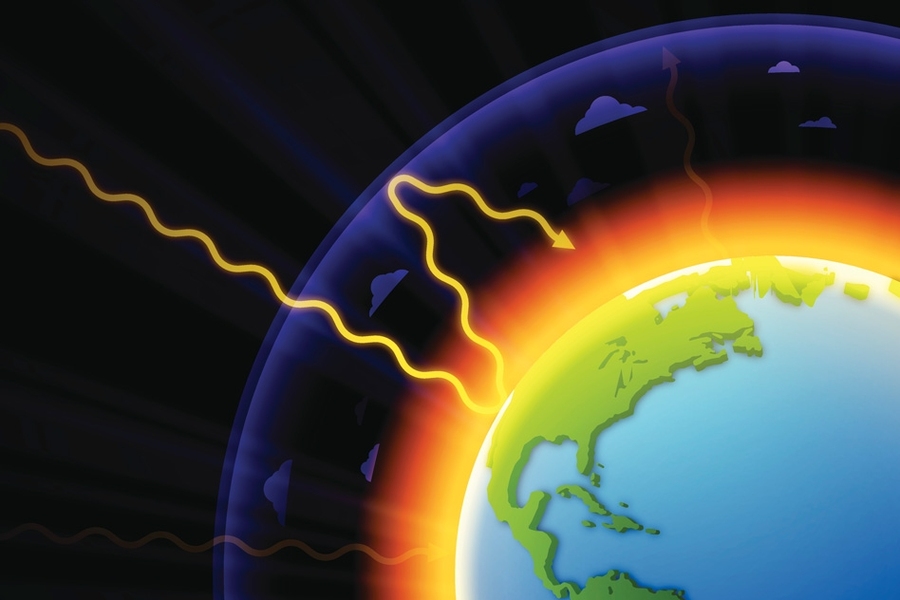

Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology

Warm On Top Cold Below Unexpected Greenhouse Gas Effect In Lakes

Greenhouse Effect Model Science Exhibition Project Diy School Fair Project Youtube

Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect

An Idealized Model Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Source Ipcc Wg1 Download Scientific Diagram

Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases

What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today

An Idealized Model Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Source Ipcc Wg1 Download Scientific Diagram
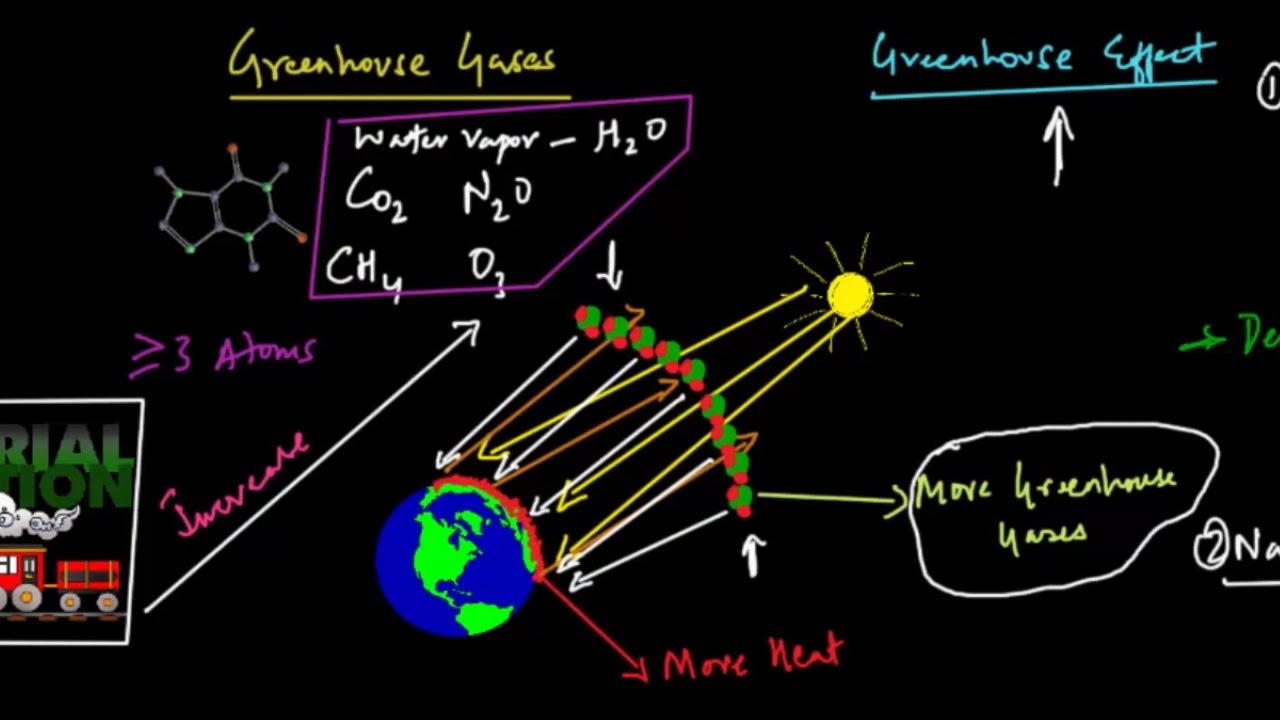
Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube
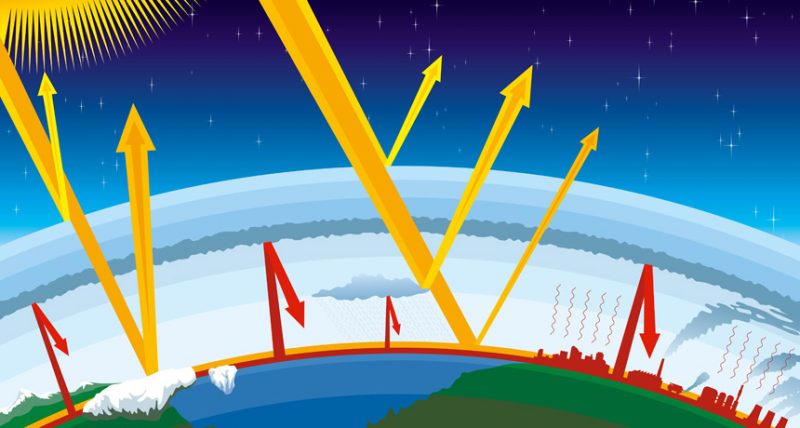

Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

2d Greenhouse Gas Lab
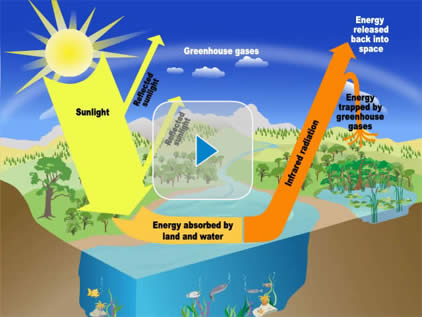
The Greenhouse Effect A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



